Difference Between BI and Data Science

- Data Science and Business Intelligence (BI) both deal with analyzing data but serve different purposes.
- BI focuses on past and present data, helping businesses track performance and make informed decisions based on historical trends.
- It uses dashboards, reports, and data visualisation tools like Power BI and Tableau to provide insights into what has happened and why.
- Data Science goes beyond BI by using advanced techniques like machine learning and predictive analytics to analyse data and forecast future trends.
- It works with both structured and unstructured data, using tools like Python, R, and AI algorithms
- Follow the below content you will get a detailed explanation of the difference between bi and data science.
- Hope this blog helps to find your answers please read the total blog.
Get Pdf version of this article here👇
What is the Difference Between BI and Data Science?
The bellowed content explained the major difference between BI and Data Science.
| Feature | Data Science | Business Intelligence (BI) |
| Purpose | Predicts future trends and solves complex problems using data | Analyzes past and current data to provide insights for decision-making. |
| Focus | Answers “What will happen?” and “What should we do next?” | Answers “What happened?” and “Why did it happen?” |
| Techniques Used | Machine learning, AI, deep learning, statistical modeling, predictive analytics, neural networks. | Data visualization, reporting, dashboards, descriptive analytics, OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) |
| Data Type | Structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data (text, images, videos, sensor data, social media, logs). | Mostly structured data (organized in databases, spreadsheets, and relational databases) |
| Tools Used | Python, R, TensorFlow, Scikit-learn, Apache Spark, Hadoop, Jupyter Notebook, Google Colab. | Power BI, Tableau, SQL, QlikView, Google Data Studio, Microsoft Excel, SAP BI. |
| Out come | Creates predictive models, finds hidden patterns, optimizes business processes, automates decision-making, and detects anomalies. | Provides reports, dashboards, and real-time/historical data insights for operational efficiency and business strategy. |
| Application Areas | Healthcare (disease prediction), finance (fraud detection, risk analysis), e-commerce (recommendation systems), social media (trend analysis), cybersecurity (threat detection), logistics (route optimization) | Sales tracking, financial reporting, inventory management, customer behavior analysis, performance monitoring, HR analytics. |
| Decision Making | Proactive – helps businesses predict trends, make future decisions, and automate processes. | Reactive – helps businesses analyze past performance and optimize current operations |
| End Users | Data scientists, AI engineers, analysts, researchers, machine learning engineers, software engineers. | Business analysts, executives, managers, decision-makers, non-technical business users |
| Nature of work | Requires coding, mathematical skills, and a deep understanding of data algorithms, AI, and statistical techniques | Mostly drag-and-drop tools, SQL queries, and dashboard/report building with minimal coding. |
| Complexity | More complex due to advanced algorithms, statistical modeling, AI-driven techniques, and deep learning models. | Easier to use, as it focuses on business reporting, visualizations, and descriptive analytics. |
| Processing speed | Uses real-time and batch processing with advanced computation models | Primarily batch processing and real-time reporting but with less complexity |
| Scalability | Can handle large-scale, high-volume data from multiple sources, including IoT, cloud, and big data technologies | Works well for structured business data but may face challenges with unstructured and big data |
| Business Impact | Drives innovation, improves efficiency, and helps businesses gain a competitive edge through AI and automation | Enhances operational efficiency, monitors KPIs, and provides better visibility into business performance |
What is Data Science(DS)?
- Data Science is the process of extracting meaningful insights from raw data using various techniques such as statistics, machine learning, and data analysis.
- It combines programming, mathematics, and domain expertise to solve complex problems and make data-driven decisions. Data Science is widely used across industries to enhance business operations, improve decision-making, and automate processes.
Key Components of Data Science?
- Data Collection: Gathering data from various sources like databases, websites, and sensors.
- Data Cleaning & Processing: Removing errors, handling missing values, and organizing data for analysis.
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA): Understanding data patterns, trends, and relationships.
- Machine Learning & AI: Building models to predict outcomes and automate decision-making.
- Data Visualization: Presenting insights using graphs, charts, and dashboards.
Tools Used in Data Science?
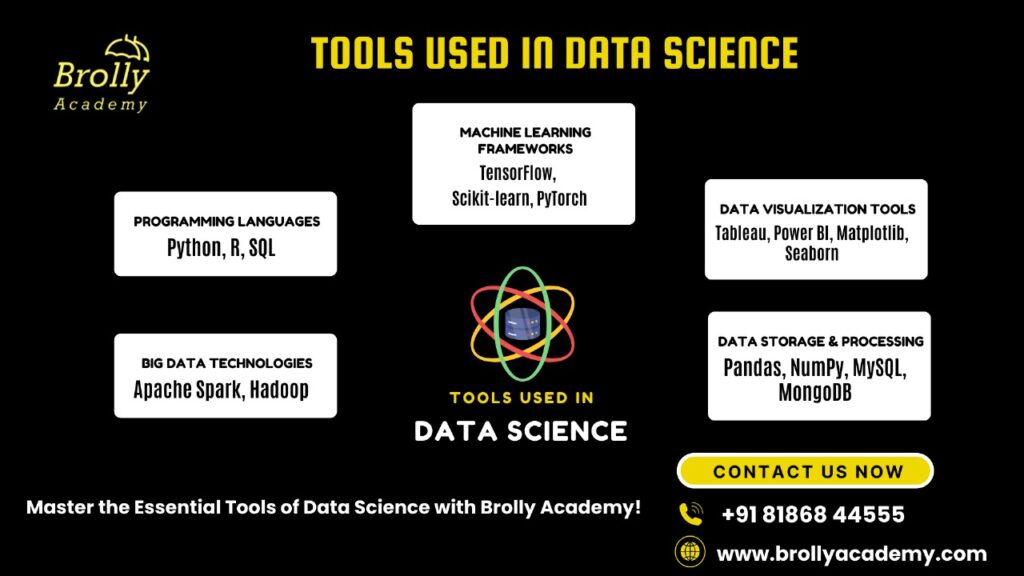
- Programming Languages: Python, R, SQL
- Machine Learning Frameworks: TensorFlow, Scikit-learn, PyTorch
- Data Visualization Tools: Tableau, Power BI, Matplotlib, Seaborn
- Big Data Technologies: Apache Spark, Hadoop
- Data Storage & Processing: Pandas, NumPy, MySQL, MongoDB
Applications of Data Science?
- Healthcare:Predicting diseases, analyzing medical images, and discovering new drugs.
- Finance: Fraud detection, stock market prediction, and risk assessment.
- E-commerce: Personalized recommendations, customer segmentation, and dynamic pricing.
- Marketing: Customer sentiment analysis, targeted advertising, and sales forecasting.
- Social Media: Content recommendations, fake news detection, and chatbots.
- Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, and automation.
- Cybersecurity: Threat detection, anomaly detection, and risk mitigation.
Advantages of Data Science?
- Improves Decision Making: Provides data-driven insights for businesses and organizations.
- Automates Tasks: Reduces manual effort by using AI and machine learning.
- Enhances Customer Experience: Delivers personalized recommendations and better user engagement.
- Detects Fraud & Security Threats: Identifies unusual patterns to prevent cyber attacks.
- Optimizes Business Processes: Helps organizations save costs and improve efficiency.
Is business intelligence in demand?
What is Business Intelligence (BI)?
Business Intelligence (BI) is the process of collecting, analyzing, and visualizing data to help businesses make informed decisions. It focuses on historical and current data to identify trends, measure performance, and improve business strategies. BI transforms raw data into meaningful insights using dashboards, reports, and data visualization tools to support decision-making.
Key Components of Business Intelligence(BI)?
- Data Collection: Gathering data from multiple sources like databases, CRM systems, and spreadsheets.
- Data Integration & Cleaning: Organizing and structuring data for analysis.
- Data Analysis & Reporting: Analyzing data to uncover trends and patterns.
- Dashboards & Visualization: Presenting insights using charts, graphs, and reports.
- Performance Monitoring: Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success.
Tools Used in Business Intelligence(BI)?
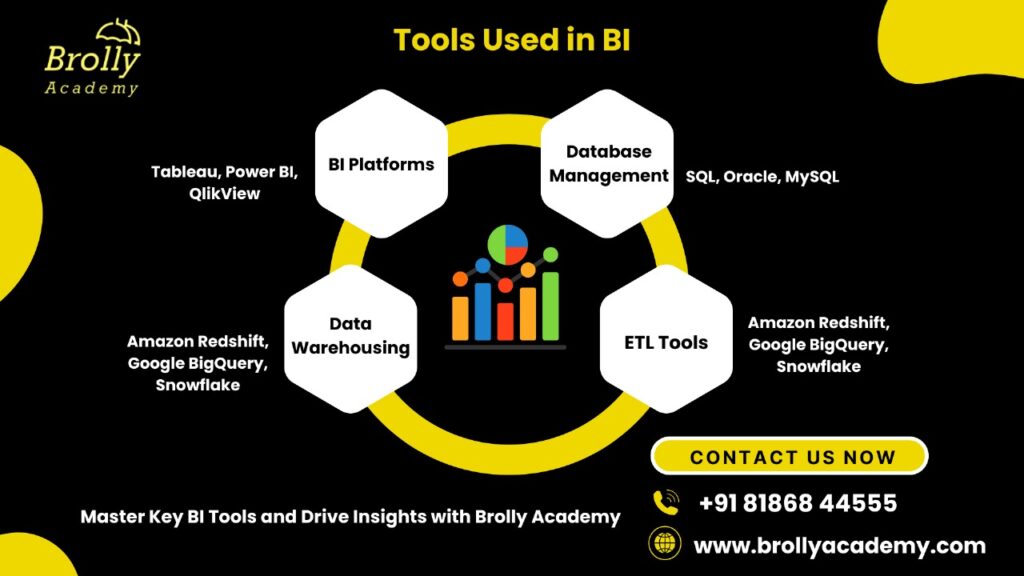
- BI Platforms: Tableau, Power BI, QlikView
- Database Management: SQL, Oracle, MySQL
- Data Warehousing: Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, Snowflake
- ETL Tools (Extract, Transform, Load): Apache Nifi, Talend, Informatica.
Applications of Business Intelligence(BI)?
- Retail & E-commerce: Sales analysis, inventory management, customer insights.
- Finance & Banking: Risk assessment, fraud detection, financial reporting.
- Healthcare: Patient data analysis, hospital performance tracking.
- Marketing: Customer segmentation, campaign performance tracking.
- Manufacturing: Supply chain optimization, production efficiency monitoring.
- Telecommunications: Network performance monitoring, customer churn analysis.
Advantages of Business Intelligence?
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Helps businesses make informed and strategic decisions.
- Real-Time Insights: Provides up-to-date information for quick actions.
- Improved Efficiency: Automates reporting and analysis to save time.
- Better Customer Understanding: Helps businesses understand customer behavior and preferences.
- Performance Monitoring: Tracks KPIs to measure business success.
Which is better
Data Science(DS) Career Path vs Business Intelligence (BI) Career Path?
Data Science Career Path?
Data Science: A multidisciplinary field that applies scientific techniques, algorithms, processes, and systems to derive insights and knowledge from both structured and unstructured data.. Data scientists are expected to build models and use algorithms to predict future trends or behaviors, ultimately aiding business decision-making processes.
Key Roles in Data Science?
- Data Scientist: The primary role in data science, where you analyze complex data, build predictive models, and design experiments.
- Data Analyst: Focuses on interpreting data and generating actionable insights through statistical analysis.
- Machine Learning Engineer: Implements machine learning algorithms to solve specific business problems.
- Data Engineer: Designs, constructs, and maintains systems and architectures for data generation, collection, and storage.
- AI Specialist: Works on the development of artificial intelligence applications using machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks.
Skills Required?
- Strong knowledge of programming languages like Python, R, and SQL.
- Proficiency in machine learning, deep learning, and AI.
- Expertise in data cleaning, data wrangling, and visualization tools (e.g., Tableau, Power BI).
- Knowledge of statistics and mathematics to interpret data and build models.
Knowledge of big data tools: Proficiency in technologies such as Hadoop and Spark
Tools/Technologies?
Python, R, TensorFlow, PyTorch, Apache Hadoop, Spark, SQL, NoSQL, and Big Data Tools.
Career Growth
- Data science offers substantial career growth, with salaries typically higher than most other tech roles due to the specialized skill set required.
- There are a variety of industries you can work in, including healthcare, finance, e-commerce, and tech.
Business Intelligence Career Path?
Business Intelligence (BI) is the process of using data analysis tools and techniques to help companies make informed business decisions. While data science is predictive and algorithm-based, BI primarily focuses on analyzing historical data to identify trends and patterns to inform business strategy.
Key Roles in BI?
- BI Analyst: Works with historical data, creating reports, dashboards, and visualizations that help business leaders make data-driven decisions.
- BI Developer: Develops and maintains BI solutions, integrating data sources, and creating custom reporting solutions.
- BI Manager: Oversees BI strategies, managing teams of analysts and developers to ensure that data insights align with business goals.
- Data Visualization Expert: Specializes in creating interactive dashboards and visual representations of data to facilitate understanding and decision-making.
Skills Required?
- Strong expertise in BI tools such as Tableau, Power BI, and QlikView.
- Knowledge of data warehousing, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, and database management.
- Proficiency in SQL for querying databases.
- Understanding of data modeling and reporting techniques.
- Strong analytical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills.
Tools/Technologies?
- Power BI, Tableau, SQL, Excel, Oracle, Qlik, and ETL Tools.
Career Growth
BI roles tend to be a bit more established than data science roles, but there’s a growing demand for BI professionals as businesses continue to rely on data for strategic decision-making. While salaries might not be as high as those in data science, the career is stable and offers room for growth, particularly in leadership roles like BI Managers.
How business intelligence and data science work together
Business Intelligence (BI) and Data Science (DS) work together to transform raw data into actionable insights by combining historical analysis (BI) with predictive analytics (DS). Here’s how they complement each other
- Data Collection & Preparation – BI gathers, cleans, and structures data from multiple sources, providing a foundation for Data Science models.
- Descriptive vs Predictive Analytics – BI analyzes past data to create reports and dashboards, while DS applies machine learning to predict future trends.
- Improved Decision-Making – BI provides real-time insights for immediate action, whereas DS offers deeper analysis to optimize long-term strategies.
- Model Deployment & Visualization – Data Science models are integrated into BI tools, allowing businesses to interact with predictions through dashboards.
- Continuous Improvement – BI helps track and measure the effectiveness of Data Science models, enabling refinement and better forecasting.
Applications of Business Intelligence (BI) and Data Science
Business Intelligence (BI) Applications?
BI helps businesses analyze historical data, monitor performance, and improve decision-making using dashboards and reports.
Retail & E-Commerce
- Sales performance analysis
- Inventory and supply chain management
- Customer segmentation and behavior analysis
Finance & Banking
- Risk management and fraud detection
- Financial reporting and budgeting
- Customer credit analysis
Healthcare
- Hospital performance tracking
- Patient records management
- Insurance claim analysis
Marketing & Sales
- Campaign performance tracking
- Lead conversion rate analysis
- Customer satisfaction and feedback analysis
Manufacturing
- Production efficiency monitoring
- Supply chain optimization
- Equipment maintenance tracking
Human Resources
- Employee performance evaluation
- Workforce planning and salary analysis
- Recruitment analytics
Telecommunications
- Customer churn analysis
- Network performance monitoring
- Revenue forecasting
Education
- Student performance tracking
- Institutional ranking and benchmarking
- Course popularity analysis
Data Science Applications?
Data Science is used to predict future trends, automate decision-making, and uncover hidden patterns using AI and machine learning.
Healthcare
- Disease prediction and diagnosis
- Personalized medicine and drug discovery
- Medical image analysis (MRI, X-ray)
Finance & Banking
- Algorithmic trading and stock market prediction
- Credit scoring and risk analysis
- Fraud detection using machine learning
E-Commerce & Retail
- Personalized product recommendations (Amazon, Netflix)
- Demand forecasting and dynamic pricing
- Chatbots for customer support
Social Media & Marketing
- Sentiment analysis and brand monitoring
- Influencer marketing and trend analysis
- Fake news detection
Cybersecurity
- Threat detection and anomaly detection
- Identity verification and fraud prevention
- AI-powered security automation
Manufacturing & Logistics
- Predictive maintenance for equipment
- Route optimization and logistics planning
- Quality control using AI-based image processing
Self-Driving Cars & Robotics
- Autonomous vehicle navigation (Tesla, Waymo)
- AI-powered robotic automation
- Smart traffic management systems
Entertainment & Media
- Content recommendation systems (Spotify, YouTube)
- Automated video editing and deepfake detection
- Sports analytics and player performance prediction
Agriculture
- Precision farming using drones and AI
- Crop disease prediction and yield forecasting
- Soil and weather analysis
Education & EdTech
- AI-driven personalized learning (Duolingo, Coursera)
- Automated grading and student performance prediction
- AI chatbots for virtual tutoring
Role of Data Science in Business Intelligence (BI)
Data Science plays a crucial role in Business Intelligence (BI) by enhancing data-driven decision-making, optimizing processes, and improving business strategies. Here are the key roles of Data Science in BI
- Advanced Data Analysis – Data Science uses statistical and machine learning techniques to analyze large datasets, uncovering hidden patterns and trends.
- Predictive Analytics – Helps businesses forecast future trends, customer behaviors, and market demands, allowing proactive decision-making.
- Data-Driven Decision Making – Enables businesses to make informed decisions based on data insights rather than intuition.
- Customer Insights & Personalization – Identifies customer preferences and behaviors, helping businesses improve customer experience and marketing strategies.
- Automation of BI Processes – AI and machine learning automate reporting and analytics, reducing manual effort and improving accuracy.
- Fraud Detection & Risk Management – Detects anomalies in financial transactions and business operations to prevent fraud and mitigate risks.
- Real-Time Analytics – Allows businesses to monitor real-time data and make quick decisions based on up-to-date information.
- Optimization of Business Operations – Enhances supply chain management, inventory optimization, and resource allocation through data-driven insights.
- Competitive Advantage – Businesses using Data Science in BI gain a competitive edge by identifying market opportunities and optimizing performance.
- Visualization & Reporting – Data Science improves BI dashboards with interactive and visual reports, making data interpretation easier for stakeholders.
What is the salary of data science vs business intelligence? need answer
In India, the compensation for Data Scientists and Business Intelligence (BI) Analysts varies based on factors such as experience, location, and industry. Here’s a comparative overview
Data Scientist Salaries?
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): Approximately ₹3,00,000 to ₹7,00,000 per annum ($3,600 to $8,500)
- Mid-Level (3-5 years): Around ₹8,00,000 to ₹15,00,000 per annum ($9,700 to $18,200).
- Senior-Level (5+ years): Between ₹16,00,000 to ₹30,00,000 or more per annum ($19,400 to $36,400+).
Business Intelligence Analyst Salaries?
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): Approximately ₹3,20,000 to ₹4,00,000 per annum ($3,900 to $4,900).
- Mid-Level (2-5 years): Around ₹6,00,000 to ₹10,00,000 per annum ($7,300 to $12,100).
- Senior-Level (5+ years): Between ₹12,00,000 to ₹18,00,000 or more per annum ($14,500 to $21,800+).
Key Factors Influencing Salaries
- Experience: Higher experience often leads to increased compensation.
- Location: Major cities like Bangalore, Mumbai, and Hyderabad tend to offer higher salaries compared to other regions.
- Industry: Sectors such as Financial Services, IT, and E-commerce typically provide more competitive salaries.
- Skills and Certifications: Proficiency in relevant tools and technologies, along with certifications, can enhance earning potential.
Which One Should You Learn? Data Science or Business Intelligence (BI)?
Deciding whether to learn Data Science or Business Intelligence (BI) depends on your interests, career goals, and the skills you want to develop. Here’s a guide to help you choose
1. Learn Data Science if
- You enjoy working with large, complex datasets and want to build models to predict future outcomes.
- You’re interested in machine learning, artificial intelligence, and deep learning. Data Science involves using algorithms and AI to analyze and interpret data.
- You want to work in fields like AI, healthcare, cybersecurity, e-commerce, or finance. Data Science is essential in these areas to identify patterns and make automated decisions.
- You like solving problems and want to make proactive decisions using data to optimize and improve business operations.
- You have strong mathematical, statistical, and programming skills. Data Science involves coding (Python, R), using machine learning algorithms, and applying complex statistical models.
- You’re interested in working on futuristic technologies, such as self-driving cars, AI-powered systems, and robotics.
Skills to Focus on for Data Science
- Programming (Python, R, SQL)
- Machine learning and AI algorithms
- Data wrangling and cleaning
- Deep learning and neural networks
- Big data tools (Hadoop, Spark)
- Data visualization (Matplotlib, Seaborn, Tableau)
2. Learn Business Intelligence (BI) if
- You prefer working with structured data (e.g., databases, spreadsheets) to generate insights that inform business decisions.
- You want to focus on analyzing historical and current data to track performance, monitor KPIs, and create reports for decision-makers.
- You enjoy creating interactive dashboards and visual reports that summarize complex data for non-technical audiences.
- You want to focus on business decision-making using historical data to optimize current operations rather than predict future trends.
- You have a knack for storytelling through data. BI involves creating visualizations and reports that communicate business insights clearly.
- You prefer using low-code/no-code tools to build reports and dashboards rather than coding complex machine learning models.
Skills to Focus on for BI
- Data visualization tools: Experience with tools like Power BI, Tableau, and Google Data Studio.
- SQL for querying databases
- Data reporting and dashboard creation
- Business process analysis and KPI tracking
- Basic statistical analysis
- Knowledge of ERP and CRM systems (e.g., SAP, Salesforce)
Key Differences in Data Science and Business Intelligence Career Path?
Data Science:
- Job Roles: Data Scientist, Machine Learning Engineer, AI Engineer, Data Engineer, Research Scientist, Deep Learning Engineer.
- Industries: Healthcare, Finance, E-commerce, AI, Technology, Cybersecurity, Autonomous Vehicles, Manufacturing, Sports Analytics.
- Career Growth: High demand for professionals with deep technical expertise in machine learning, AI, and big data
Business Intelligence
- Job Roles: BI Analyst, BI Developer, BI Consultant, Data Analyst, Data Reporting Specialist.
- Industries: Retail, Marketing, Finance, Healthcare, HR, Manufacturing, Education.
- Career Growth: Strong demand for professionals who can interpret and present data insights to inform business decisions.
When to Choose Data Science Over BI
- If you’re passionate about working with algorithms and building predictive models.
- If you want to be involved in AI-driven automation and problem-solving across various industries.
- If you’re comfortable with advanced statistical methods, coding, and programming.
- If you aspire to work in industries that rely heavily on advanced analytics (like healthcare, e-commerce, and finance).
When to Choose BI Over Data Science
- If you prefer working with business data to provide actionable insights that influence strategic decisions.
- If you enjoy creating visual reports and dashboards that tell a clear story with data.
- If you have a strong understanding of business operations and want to focus on improving efficiency.
- If you prefer less coding and more tool-based approaches like Tableau, Power BI, and Excel.
Conclusion
Data Science focuses on predicting future trends, utilizing machine learning, artificial intelligence, and advanced analytics to automate processes and make data-driven predictions. It’s ideal for those who enjoy working with large datasets, coding, and solving complex problems.
Business Intelligence (BI), on the other hand, focuses on analyzing historical and current data to generate insights, track performance, and support business decisions. It’s more about creating dashboards, visual reports, and offering actionable insights for business optimization.
When deciding which one to learn, consider your interest in technical skills (Data Science) versus your preference for business insights and decision-making (BI). Both fields are in high demand and offer exciting career paths. You can also choose to start with one and later transition to the other, as the two fields complement each other.
FAQ’s
Difference between Power BI and Data Science
1. What is Data Science?
Data Science is the field that uses statistical analysis, machine learning, and algorithms to extract insights from structured and unstructured data. It helps businesses predict future trends, make data-driven decisions, and automate processes using AI and advanced analytics.
2. What is Business Intelligence (BI)?
- Business Intelligence (BI) refers to the technologies, tools, and practices used to analyze and visualize historical and current business data. It helps businesses monitor performance, track KPIs, generate reports, and make strategic decisions based on past data.
3. What is the difference between BI and data science?
BI focuses on analyzing past and present data using dashboards and reports to support business decisions. It provides insights into what happened and why.
Data Science goes beyond BI by using machine learning, AI, and predictive analytics to analyze data and forecast future trends. It works with both structured and unstructured data for deeper insights and automation.
4. Can a business intelligence analyst become a data scientist?
- Yes, a Business Intelligence (BI) analyst can become a Data Scientist by learning programming (Python, R), machine learning, statistical analysis, and AI techniques. Since BI analysts already have strong data handling and analytical skills, transitioning to Data Science requires gaining expertise in predictive modeling, advanced analytics, and coding.
5. What is the salary of data science vs business intelligence?
Data Scientist Salary: In India, ₹13,50,000 ($18,000); in the US, $118,045.
BI Analyst Salary: In India, ₹8,50,000 ($11,000); in the US, $101,398.
Salaries vary based on experience, location, and industry.
6. What are the job opportunities in Data Science?
Some common job titles in Data Science include:
- Data Scientist
- Machine Learning Engineer
- Data Analyst
- AI Engineer
- Data Engineer
- Research Scientist
7. What are the job opportunities in Business Intelligence?
Some common job titles in BI include:
- BI Analyst
- BI Developer
- BI Consultant
- Data Analyst
- Data Reporting Specialist
8. Can I learn both Data Science and BI?
Yes, many professionals start with Business Intelligence to understand business data and then transition into Data Science to work on predictive models and machine learning. Both fields complement each other and can be learned sequentially or in parallel.
9. Which one is better to learn: Data Science or BI?
- Data Science is better for those who want to work with machine learning, AI, and predictive modeling.
- BI is better for those who prefer working with visualizations, dashboards, and making data-driven decisions using historical data.
- Both fields are important, so your choice depends on your interest in technical skills (Data Science) vs. business insights (BI).
10. What skills are required for Data Science?
- Programming languages (Python, R, SQL)
- Machine learning algorithms and frameworks (TensorFlow, Scikit-learn)
- Statistical analysis and probability
- Big data technologies (Hadoop, Spark)
- Data wrangling and cleaning techniques
- Data visualization tools (Matplotlib, Seaborn, Tableau)
Brolly Academy offers C and C ++ Training| | React Training, | HTML & CSS Training, | MEAN Stack Development in Hyderabad.

