Applications Of Artificial Intelligence In Robotics
Applications Of Artificial Intelligence In Robotics
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized various industries, and one of its most groundbreaking applications is in robotics.
- AI in robotics refers to the integration of intelligent algorithms that enable machines to learn, adapt, and perform tasks autonomously.
- Unlike traditional robots that follow pre-programmed instructions, AI-driven robots can analyze data, make decisions, and improve their performance over time through machine learning and other AI technologies.
- From industrial automation to healthcare, military, and space exploration, AI-powered robots are transforming the way tasks are performed.
- These advanced robots are capable of understanding their environment, recognizing patterns, and even making independent decisions, making them valuable assets in various fields.
- The continuous evolution of AI is pushing robotics to new heights, making them more efficient, adaptable, and intelligent.
Importance of AI in Modern Robotics
The significance of AI in robotics cannot be overstated. Traditional robotics relied on rigid programming and predefined tasks, limiting their adaptability. However, AI has empowered robots with cognitive abilities, enabling them to:
- Perform complex tasks autonomously: AI-driven robots can analyze and react to real-time data, making them useful in dynamic environments like self-driving cars and industrial automation.
- Improve efficiency and productivity: AI-powered automation in industries leads to higher accuracy, reduced operational costs, and increased production rates.
- Enhance human-robot collaboration: With AI, robots can understand human commands, work alongside people safely, and assist in hazardous environments.
- Adapt and learn: AI allows robots to learn from past experiences and improve their performance over time, reducing the need for constant reprogramming.
How AI Enhances Robotic Capabilities
- Autonomous Decision-Making: AI-powered robots can process data in real time and make independent decisions, eliminating the need for constant human intervention.
- Computer Vision: Robots equipped with AI-based vision systems can recognize objects, detect anomalies, and navigate complex environments.
- Machine Learning: AI enables robots to learn from experience, improving their performance in tasks such as speech recognition, predictive maintenance, and quality control.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI allows robots to understand and respond to human speech, making them effective in customer service, personal assistance, and collaborative workspaces.
- Predictive Analytics: AI helps robots anticipate future events, such as predicting equipment failures in industrial settings or forecasting crop growth in agriculture.
Key AI Technologies Used in Robotics
AI in robotics is powered by several advanced technologies that enable autonomous decision-making, perception, and adaptability. Some of the most important AI technologies in robotics include:
1. Machine Learning (ML)
- Machine learning allows robots to learn from data and improve their performance over time. By analyzing vast amounts of information, robots can recognize patterns, make predictions, and adjust their actions accordingly.
- ML algorithms are widely used in robotic automation, predictive maintenance, and adaptive control systems.
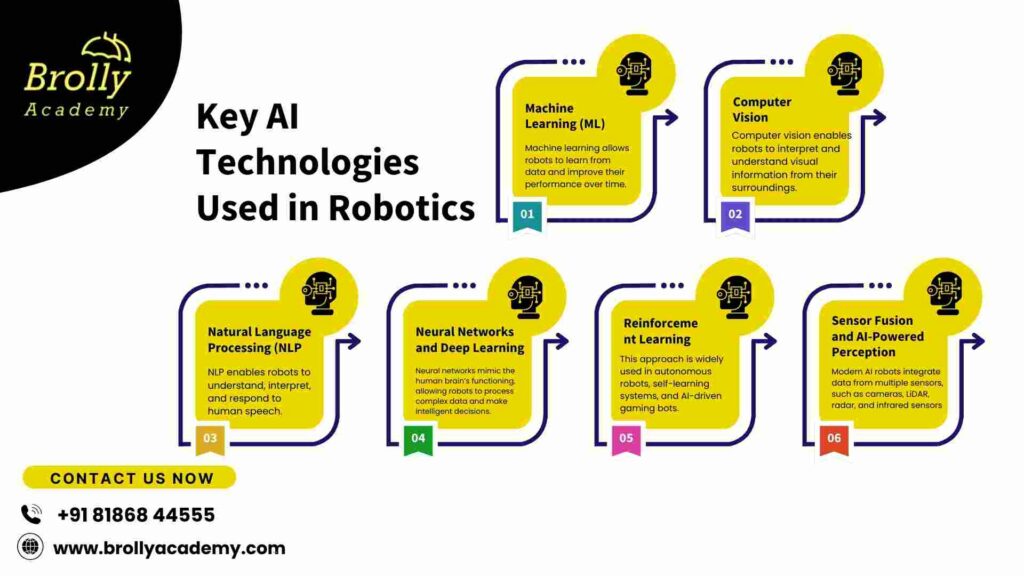
2. Computer Vision
- Computer vision enables robots to interpret and understand visual information from their surroundings.
- AI-powered cameras and sensors help robots recognize objects, detect obstacles, and perform tasks such as quality control in manufacturing, facial recognition in security systems, and autonomous navigation in self-driving cars.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- NLP enables robots to understand, interpret, and respond to human speech. AI chatbots, virtual assistants, and customer service robots rely on NLP to communicate effectively with users.
- This technology is essential for voice-controlled systems, human-robot interaction, and multilingual support in robotics.
4. Neural Networks and Deep Learning
- Neural networks mimic the human brain’s functioning, allowing robots to process complex data and make intelligent decisions.
- Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, enables robots to recognize speech, translate languages, and classify images with high accuracy.
- This technology is crucial in facial recognition, robotic vision, and AI-driven automation.
5. Reinforcement Learning
- Reinforcement learning is an AI technique where robots learn through trial and error by receiving rewards or penalties for their actions.
- This approach is widely used in autonomous robots, self-learning systems, and AI-driven gaming bots.
6. Sensor Fusion and AI-Powered Perception
- Modern AI robots integrate data from multiple sensors, such as cameras, LiDAR, radar, and infrared sensors, to develop a comprehensive understanding of their environment.
- This capability enhances robotic navigation, object detection, and real-time decision-making in various applications, including autonomous vehicles and industrial automation.
- Self-driving cars: AI helps autonomous vehicles navigate roads, avoid obstacles, and make driving decisions in real time.
- Industrial automation: AI-driven robots optimize manufacturing processes by adjusting their operations based on sensor inputs and real-time data.
- Healthcare robotics: AI-powered surgical robots assist doctors by making precise movements and adjusting techniques based on patient conditions.
- AI-powered drones: Drones use AI to navigate, track objects, and make independent flight decisions for applications like surveillance, delivery, and disaster response.
Applications Of Artificial Intelligence In Robotics
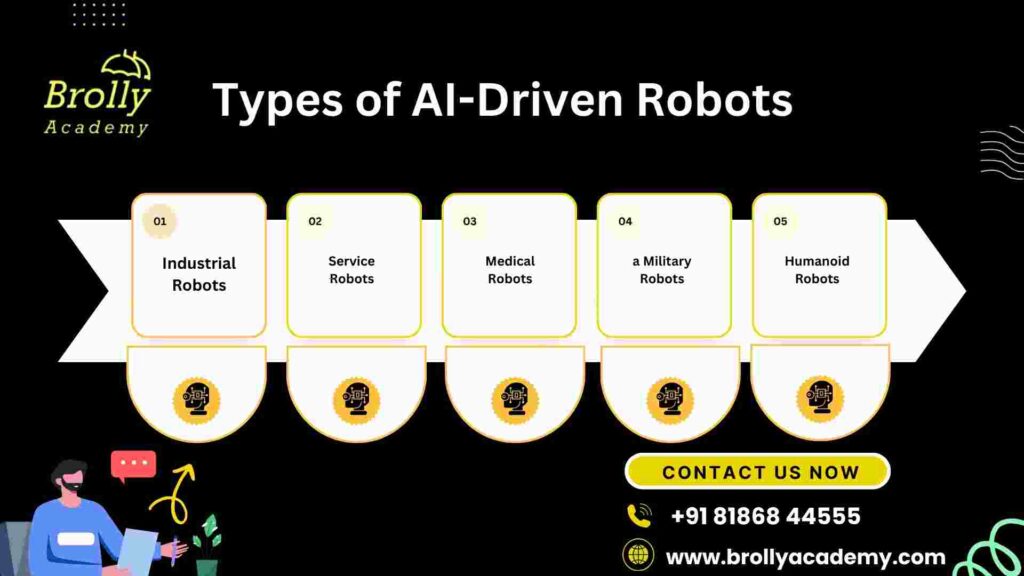
Types of AI-Driven Robots
1. Industrial Robots
Applications of Industrial Robots:
- Robots equipped with AI-driven vision systems can detect defects and assemble products with high precision.
- AI helps in analyzing machine performance, predicting failures, and reducing downtime.
- AI-driven robots can move heavy materials in warehouses and factories, optimizing logistics.
Companies like Tesla, Amazon, and BMW extensively use AI-powered industrial robots to streamline their manufacturing processes.
2. Service Robots
Applications of Service Robots:
- AI-powered robots serve customers in hotels, restaurants, and shopping malls by taking orders and providing assistance.
- AI chatbots and humanoid robots are used in banks and service centers to interact with customers.
- AI-driven security robots monitor premises, detect suspicious activity, and alert authorities.
Popular examples include SoftBank’s Pepper Robot and Amazon’s Astro Robot, which assist in customer service and home automation.
3. Medical Robots
Applications of Medical Robots:
- Robotic surgical systems like da Vinci Surgical System enable minimally invasive surgeries with high precision.
- AI-powered robots assist elderly patients by monitoring their health, reminding them to take medications, and providing companionship.
- AI-driven exoskeletons help patients recover from injuries by providing physical therapy and mobility support.
Medical robotics is a growing field, improving patient outcomes and making healthcare more efficient.
4. Military Robots
Applications of Military Robots:
- Drones equipped with AI can detect threats, track enemy movements, and conduct reconnaissance missions.
- AI-driven robots are being developed to support soldiers in combat, reducing human casualties.
- AI-enabled robots help defuse bombs and handle dangerous materials.
Countries like the USA and China are heavily investing in AI-driven military robotics to enhance their defense capabilities.
5. Humanoid Robots
Applications of Humanoid Robots:
- AI-powered humanoid robots greet customers, answer queries, and provide information in malls, banks, and hotels.
- Humanoid robots assist in teaching and scientific research by demonstrating human-like behaviors.
- AI-driven humanoid robots provide emotional support and assistance to elderly individuals or people with disabilities.
Notable examples include Sophia by Hanson Robotics and ASIMO by Honda, which showcase human-like communication and movement.
- For a detailed analysis of AI’s impact on automation, visit the IEEE Robotics and Automation Society
Applications Of Artificial Intelligence In Robotics
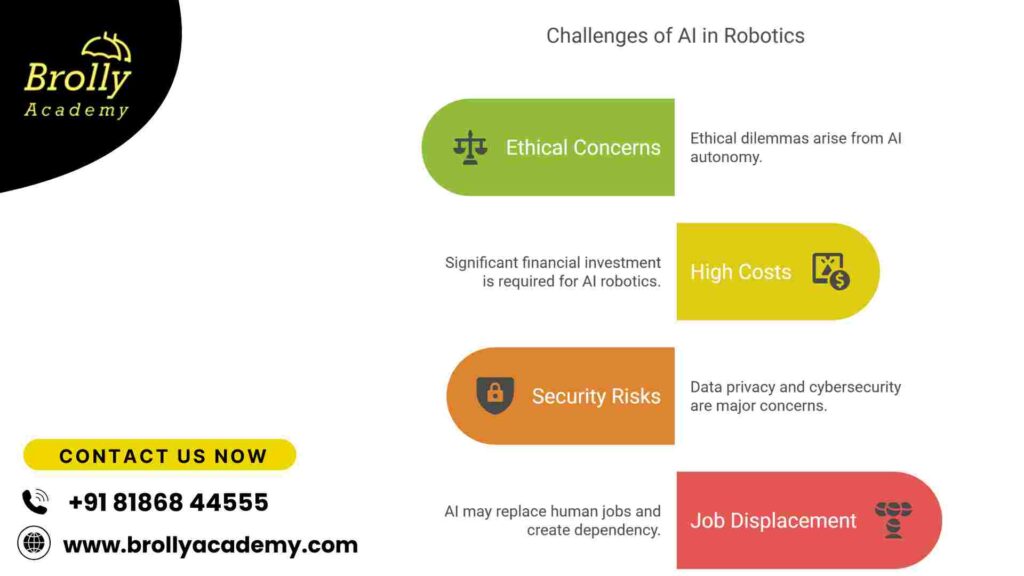
Challenges and Limitations of AI in Robotics
1. Ethical Concerns and Risks
Lack of Moral and Ethical Judgment
- AI-driven robots lack human emotions and moral reasoning, leading to potential ethical dilemmas in decision-making.
- Autonomous weapons and AI-driven military robots raise concerns about accountability and responsible use.
- AI-powered healthcare robots may struggle to make ethical medical decisions in life-or-death situations.
Bias in AI Algorithms
- AI models are trained on data, which may contain biases, leading to discriminatory behavior in robotic systems.
- AI-powered hiring robots may unintentionally favor certain demographics, leading to unfair recruitment processes.
- Bias in facial recognition algorithms used in security robots can result in wrongful identifications.
Ethical considerations must be prioritized in AI development to ensure fair and responsible deployment of AI-driven robotics.
2. High Costs of AI-Driven Robotic Systems
Expensive Hardware and Software Development
- AI-driven robots require advanced sensors, high-performance computing, and sophisticated AI algorithms, making them costly to develop.
- Companies must invest in expensive machine learning infrastructure, such as GPUs and cloud computing.
- Regular software updates and AI model retraining add to the long-term costs.
Limited Accessibility for Small Businesses
- High costs make AI-powered robots inaccessible for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
- Large corporations can afford AI automation, creating a competitive gap in industries.
- Efforts are needed to develop cost-effective AI robotic solutions to increase adoption across all business sizes.
While AI robotics can enhance efficiency, their high costs remain a significant barrier to widespread implementation.
3. Security and Data Privacy Concerns
Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities
- AI-powered robots are susceptible to cyberattacks, hacking, and malware threats.
- Autonomous vehicles and drones can be hijacked, leading to safety risks.
- AI-powered surveillance robots may be exploited to invade privacy or manipulate information.
Data Privacy Risks
- AI-driven service robots collect vast amounts of user data, raising concerns about data protection.
- Personal assistants like AI-powered home robots and chatbots may store sensitive information, risking data leaks.
- Regulations and policies must be enforced to protect user privacy in AI-driven robotic systems.
Ensuring robust cybersecurity and data privacy protections is essential for the safe deployment of AI-driven robots.
4. Dependency on AI and Potential Job Displacement
AI Replacing Human Jobs
- AI-driven automation in manufacturing, customer service, and logistics is reducing the need for human workers.
- Routine and repetitive jobs are at high risk of being replaced by AI-powered robots.
- The shift toward AI automation may lead to job losses and economic disparities in certain industries.
Over-Reliance on AI Systems
- Businesses may become overly dependent on AI robots, reducing human expertise and decision-making abilities.
- AI-driven failures or system malfunctions could disrupt critical operations in industries like healthcare and defense.
- A balance between AI automation and human oversight is crucial to prevent excessive reliance on robotic systems.
Future of AI in Robotics – 8 Key Points
- AI will make robots more independent, allowing them to learn, adapt, and make decisions without human intervention.
- Robots will work alongside humans more efficiently, assisting in industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and customer service.
- Medical robots will assist in surgeries, patient care, and rehabilitation, improving precision and reducing human errors.
- Self-driving cars, drones, and delivery robots will become more reliable, safe, and widely used for transportation and logistics.
- Robots will enhance home automation, helping with household chores, elderly care, and security.
- AI-powered robots will optimize manufacturing, improving efficiency, quality control, and reducing operational costs.
- As robots become more advanced, addressing ethical concerns, job displacement, and security risks will be crucial.
- AI-driven robots will assist in deep space missions, planetary exploration, and astronaut support, making space travel safer and more efficient.
Conclusion of Applications Of Artificial Intelligence In Robotics
FAQs on Applications Of Artificial Intelligence In Robotics
What is AI in robotics?
AI in robotics refers to the integration of artificial intelligence technologies like machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing (NLP) into robots, enabling them to learn, adapt, and perform tasks autonomously.


