How SEO Helps in Digital Marketing in 2026

Introduction : Why Seo Still Controls Digital Marketing in 2026
- In 2026, SEO is no longer a supporting tactic—it is the strategic core of digital marketing. Every major digital decision begins with understanding how users search, what they expect, and how they make decisions online.
- SEO provides this insight. It translates real search behavior into actionable strategies that guide content creation, paid campaigns, social messaging, website experience, and brand positioning.
- Search engines have evolved from keyword matchers into intent and experience evaluators. They now prioritize content that solves real problems, demonstrates expertise, and delivers smooth user experiences.
- This shift has pushed SEO beyond rankings into areas like user psychology, trust building, and conversion optimization. Brands that ignore SEO insights struggle with rising ad costs, low engagement, and inconsistent results.
- AI-powered search, zero-click results, and voice-based queries have not reduced SEO’s importance they have raised the standard.
- SEO now determines which sources AI trusts, summarizes, and surfaces as answers. Visibility is earned through clarity, credibility, and usefulness, not manipulation.
- Most importantly, SEO connects user intent with business outcomes. It attracts high-intent users, builds long-term authority, reduces dependency on paid ads, and delivers compounding returns.
- In an increasingly competitive and AI-driven landscape, SEO remains the most reliable, sustainable, and future-ready driver of digital marketing success.
The Evolution of Search: From Keywords to Intent, Context, and Experience:
Earlier, SEO was heavily focused on keywords what users typed into the search box. Marketers optimized pages by repeating exact-match keywords and building backlinks. However, search in 2026 is no longer about isolated words. It is about intent, context, and overall experience.
Modern search engines now understand:
- Why a user is searching (intent)
- What situation they are in (context)
- How helpful the content is (experience)
For example : Two users searching the same query may see different results based on location, device, past behavior, and urgency. Search engines evaluate whether content truly solves the user’s problem, not just whether it contains keywords. This shift has pushed SEO toward meaningful, human-first content that delivers real value instead of manipulation.
Why SEO Is No Longer a Channel, but the Foundation of Digital Marketing:
In 2026, SEO is not a separate marketing channel like social media or paid ads. Instead, it acts as the strategic backbone of all digital efforts.
Every successful digital campaign aligns with SEO principles understanding user behavior, search intent, content relevance, and trust signals.
Whether you’re running ads, posting on social media, or sending emails, users still:
- Research before buying
- Compare options on search engines
- Look for reviews, answers, and credibility
If your brand does not appear with helpful, trustworthy content during these moments, other marketing efforts lose impact.
SEO ensures that your digital presence is discoverable, credible, and consistent across all touchpoints, making it the foundation rather than an add-on.
Impact of AI Search, SGE, Voice Search, and Zero-Click Results:
AI-powered search experiences, Search Generative Experiences (SGE), voice assistants, and zero-click results have transformed how users interact with search engines. In many cases, users now get answers directly on the search results page, without clicking a website.
This does not mean SEO is dying rather, it means SEO has matured. In 2026, optimization focuses on:
- Being a trusted source AI systems rely on
- Structuring content clearly so machines can understand it
- Providing concise, accurate, and authoritative answers
Voice search has also increased conversational queries, while AI-generated summaries reward content that is clear, factual, and user-focused.
Brands that adapt their SEO strategy to these changes gain visibility even when clicks reduce, because visibility, trust, and authority matter more than traffic alone.
What Users Expect When They Search in 2026:
Users in 2026 expect more than just information they expect solutions. When someone searches, they want:
- Fast, accurate answers
- Clear explanations in simple language
- Trustworthy and updated information
- Content that matches their exact need without confusion
Users are less patient with irrelevant, outdated, or promotional content. They value experiences that respect their time and intent.
This has forced SEO to align closely with helpfulness, clarity, and authenticity, ensuring content genuinely serves the user rather than just the algorithm.
SEO as the Bridge Between User Needs and Business Goals
At its core, SEO in 2026 acts as a bridge between what users want and what businesses offer. When done correctly, SEO helps businesses understand real user problems, questions, and motivations—and then create content, products, and services that meet those needs.
For users, SEO delivers:
- Relevant answers
- Trustworthy guidance
- Better experiences
For businesses, SEO delivers:
- Qualified traffic
- Long-term visibility
- Sustainable growth and credibility

What Is Search Engine Optimization (SEO)?
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the process of improving a website so that it becomes easier for search engines to understand, trust, and show to users when they search for relevant information.
In simple terms, SEO helps your content appear in front of the right audience at the right time without paying for ads. - SEO is not just about ranking higher; it is about delivering the best possible answer or solution to a user’s query in a way that search engines can clearly interpret and recommend.
Simple Definition of SEO
- SEO is the practice of optimizing content, structure, and experience of a website to match what users are searching for and how search engines evaluate quality.
- It involves creating helpful content, organizing information clearly, improving page performance, and building trust signals so search engines can confidently rank that content. At its core, SEO is about helpfulness and relevance, not tricks or shortcuts.
Why SEO Exists in the Digital Ecosystem:
SEO exists because the internet contains billions of pages, and users need a way to find the most useful and reliable information quickly. Search engines act as information gateways, and SEO helps them decide which content deserves visibility. Without SEO, high-quality content could remain invisible, while users struggle to find accurate answers.
In the digital ecosystem, SEO plays a crucial role by:
- Helping users discover relevant solutions
- Helping search engines organize and rank content efficiently
- Helping businesses reach people who are actively searching for their products or services
Optimization vs Manipulation
True SEO is about optimization, not manipulation. Optimization means improving content and websites so they align with user intent and search engine quality standards. Manipulation, on the other hand, involves trying to game algorithms using shortcuts like keyword stuffing, low-quality backlinks, or misleading content.
In 2026, search engines are highly advanced and designed to detect manipulation easily. Practices that focus on tricks rather than value often lead to penalties or loss of trust.
Sustainable SEO focuses on:
- Clear and honest content
- Genuine usefulness
- Long-term credibility
How SEO Connects Users, Search Engines, and Businesses
SEO acts as a bridge between three key players in the digital world: users, search engines, and businesses. Users search with a goal in mind answers, solutions, or decisions. Search engines aim to deliver the most relevant and trustworthy results. Businesses want to reach users who need what they offer.
SEO aligns these goals by:
- Translating user intent into structured, understandable content
- Helping search engines interpret relevance and quality
- Allowing businesses to appear naturally when users are ready to engage
How Do Search Engines Work?
- Search Engines are designed to help users find the most accurate, relevant, and helpful information from billions of web pages in seconds.
- To achieve this, they follow a structured three-step process: Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking.
- Understanding this process is essential for SEO because every optimization effort directly supports one or more of these stages.
- In 2026, search engines rely heavily on AI, user behavior, and experience signals, making this process more intelligent than ever.

Level 1: Search Engine Crawling
Crawling is the discovery phase where search engines look for new and updated content across the web. This is done using automated programs known as bots or crawlers. These bots move from page to page by following links, just like users browsing a website.
1. What crawling means : Crawling means search engines are finding your pages and understanding that they exist. If a page is not crawled, it cannot appear in search results. Crawlers prioritize pages that are frequently updated, well-linked, and technically accessible.
2. Role of bots and crawlers : Bots analyze page structure, links, content, and technical signals. In 2026, crawlers are smarter and more selective. They focus crawl budgets on high-value pages and may ignore low-quality or duplicate content.
3. Importance of internal links and site architecture : Clear site architecture and strong internal linking help crawlers discover important pages faster. Logical navigation, clean URLs, and contextual internal links guide bots efficiently, ensuring key content is not missed.
Level 2: Search Engine Indexing
After crawling, search engines move to indexing where content is analyzed, processed, and stored in massive databases.
1. How content is stored and interpreted : During indexing, search engines evaluate what a page is about by analyzing text, headings, media, metadata, and structured data. AI systems interpret meaning, context, and topical relevance rather than relying only on keywords.
2. Common indexing challenges: Pages may fail to index due to duplicate content, thin pages, blocked resources, poor structure, or technical errors. In 2026, low-value or confusing content is often ignored even if technically accessible.
3. Role of content quality and structure: High-quality, well-structured content improves indexing accuracy. Clear headings, logical flow, and focused topics help search engines correctly categorize and retrieve content for relevant queries.
Level 3: Search Engine Ranking
Ranking determines which indexed pages appear in search results and in what order.
1. How relevance and authority are evaluated: Search engines evaluate how well a page matches user intent and how trustworthy the source is. Authority is built through content depth, expertise, and quality references from other credible websites.
2. User signals and engagement metrics : Search engines analyze real user behavior such as clicks, dwell time, and interaction patterns. Pages that satisfy users tend to maintain or improve rankings, while poor engagement signals trigger reevaluation.
3. Freshness and intent matching : For time-sensitive queries, fresh content is prioritized. For evergreen topics, regularly updated and intent-aligned content performs best. In 2026, intent matching is the most critical ranking factor—pages must fully satisfy what users are searching for.
How Does Google Order and Rank Search Results?
- Google orders and ranks search results with one primary goal: to show users the most relevant, useful, and trustworthy content for their query. In 2026, ranking is no longer about a single factor or formula.
- Instead, Google uses a complex system of signals, AI models, and contextual understanding to decide which pages deserve top visibility. These systems work together to evaluate not just what a page says, but how well it actually helps the user.
Overview of Ranking Signals:
Google employs numerous ranking signals to assess web pages. These signals include content relevance, quality, authority, page performance, usability, freshness, and trust indicators. No single signal determines rankings on its own. Instead, Google looks at the overall quality and usefulness of a page in relation to the user’s search intent.
Ranking signals work together to answer key questions:
- Does this page match what the user is searching for?
- Is the information precise, trustworthy, and current?
- Does the page provide a good user experience?
- Can this source be trusted over others?
Relevance vs Usefulness:
Relevance and usefulness are closely related but not the same. Relevance means the content matches the search query topic. Usefulness goes a step further it measures how well the content actually solves the user’s problem.
In earlier years, relevance alone could help pages rank. In 2026, usefulness is the deciding factor.
A page may be relevant but still rank lower if it:
- Repeats basic information without depth
- Fails to answer follow-up questions
- Is poorly written or confusing
Content Quality, Backlinks, and Page Experience
- Content quality remains one of the strongest ranking foundations. High-quality content is original, accurate, clearly written, and aligned with user intent. It reflects expertise, real-world understanding, and trustworthiness.
- Backlinks still matter, but their role has evolved. Google values quality over quantity. Links from credible, relevant websites act as trust signals, showing that others recognize the content as valuable. Manipulative or irrelevant links no longer help and can even harm rankings.
- Page experience is equally important. Google evaluates how users interact with a page—loading speed, mobile usability, layout stability, and ease of navigation.
- Even excellent content can underperform if the page is slow, cluttered, or difficult to use. In 2026, strong rankings require both great content and a smooth experience.
Role of Personalization and Search Context
- Google does not present identical results to all users. Search results are influenced by context and personalization, including location, device type, language, past search behavior, and timing. For example, the same query may show different results for a student, a professional, or a local user.
- This means ranking is not static. Google adjusts results to better match individual user needs. SEO today focuses less on chasing one “fixed” ranking position and more on being consistently relevant across different contexts.
How Rank Brain and AI Systems Influence Rankings
Rank Brain and other AI-driven systems play a major role in how Google understands queries and ranks results. These systems use machine learning to interpret complex searches, especially those that are new, ambiguous, or conversational.
- Machine Learning in Modern Search:
- Machine learning allows Google to improve search results based on patterns and feedback rather than manual rules alone.
- AI systems analyze large amounts of data to understand which results satisfy users and which do not. Over time, this helps Google refine rankings automatically.
- Instead of relying only on exact keywords, AI systems understand meaning, relationships, and context. This makes search more accurate and human-like, especially for long or voice-based queries.
2. Understanding User Intent and Behavior Patterns:
- AI systems study user behavior signals such as clicks, dwell time, and interaction trends to understand intent more deeply.
- If users consistently prefer certain types of content for a query, Google learns from that behavior and adjusts rankings accordingly.
- This means content must align not just with keywords, but with real user expectations. Pages that confuse, mislead, or disappoint users gradually lose visibility, even if they are technically optimized.
3. Optimizing for Experience, Not Shortcuts:
- In 2026, Google’s AI systems are highly effective at detecting shortcuts and manipulation. Tactics designed only to exploit algorithms no longer work.
- Sustainable SEO focuses on experience-first optimization clear content, honest information, strong structure, and user satisfaction.
- Websites that prioritize helpfulness, transparency, and usability naturally align with how Google’s AI systems evaluate quality. The result is long-term visibility built on trust, not temporary ranking tricks.
Understanding What Users Want in 2026
- Google has evolved far beyond matching keywords to pages. In 2026, search is deeply human-centric. Users don’t search randomly they search with intent, emotion, urgency, and expectations.
- To succeed in modern SEO, understanding what users truly want is more important than understanding algorithms. Search engines now reward brands that align with user psychology, intent, and experience rather than technical tricks.
The Psychology of Search Behavior
Users Search for Solutions, Not Keywords:
- Users do not think in SEO terms. They don’t care about keywords, rankings, or metadata. They care about solving a problem, answering a question, or making a decision.
- Whether they type a short query or a long conversational question, their goal is always clarity and resolution.
- In 2026, search engines understand this mindset very well. That’s why content written for people first performs better than content written for algorithms.
- Pages that directly address pain points, explain options clearly, and guide users toward solutions align naturally with how people search.
Micro-Moments: Know, Go, Do, Buy:
Search behavior is driven by micro-moments small but powerful intent-driven actions that happen throughout the day:
- Know: Learning or researching information
- Go: Finding a location or service nearby
- Do: Finished a task or acquired how to do something
- Buy: Making a purchase or taking action
Decision-Making Stages Supported by Search:
- Search plays a role across the entire decision-making journey:
- Awareness (understanding a problem)
- Consideration (comparing options)
- Decision (choosing a solution)
- Action (conversion or engagement)
Search Intent Types That Matter Today
Understanding intent is the backbone of SEO in 2026. Search engines classify queries based on what the user wants to achieve, not how the query is phrased.
- Informational Intent: Users want to learn or understand something. They are looking for explanations, guides, or answers. Content here should be clear, accurate, and structured to educate without overwhelming.
- Navigational Intent: Users want to reach a specific brand, website, or platform. They already know what they’re looking for. Clear branding, optimized pages, and consistency help capture this intent effectively.
- Commercial Investigation Intent: Users are evaluating options before making a decision. They compare products, services, prices, and reviews. Content that explains differences, pros and cons, and real-world use cases performs best at this stage.
- Transactional Intent: Users are ready to take action—buy, sign up, book, or contact. At this stage, clarity, trust signals, and ease of use are critical. Any friction can result in lost conversions.
How Google Evaluates Intent Using Behavior Signals
- Search engines analyze real user behavior to validate intent matching. Signals such as click patterns, engagement time, scroll depth, and return behavior help determine whether content satisfies users.
- If users consistently engage positively, the content gains visibility. If they leave quickly or search again, rankings adjust.
This feedback loop ensures that intent satisfaction not keyword placement drives rankings.
What Users Expect From Your Website
- Instant Answers With Minimal Friction : Users expect answers quickly. Long introductions, unnecessary fluff, and confusing layouts reduce trust. Clear answers near the top of the page improve satisfaction and performance.
- Clear Structure and Scannable Content: People scan before they read. Headings, short paragraphs, bullet points, and logical flow help users find what they need instantly. Well-structured content also helps search engines understand relevance better.
- Proof of Expertise and Credibility: People want to know why they should put their trust in you. Experience, accurate information, real examples, and transparent messaging signal credibility. Thin or generic content no longer works in 2026.
- Fast Loading and Mobile-First Experience : Most searches happen on mobile devices. Users expect pages to load quickly, function smoothly, and adapt perfectly to smaller screens. Performance is not optional—it is a trust factor.
- Trust Signals, Reviews, and Transparency : Users look for reassurance before engaging. Reviews, testimonials, clear policies, author credibility, and transparent business information reduce uncertainty. Trust is no longer implied—it must be demonstrated clearly.
What Are the Three Pillars of SEO?
- SEO in 2026 is built on three strong and interdependent pillars: On-Page SEO, Off-Page SEO, and Technical SEO. These pillars work together to ensure that a website is useful for users, understandable for search engines, and trustworthy in the wider digital ecosystem.
- Ignoring even one pillar can weaken overall performance, because modern SEO success depends on balance, quality, and user experience rather than isolated tactics.

On-Page SEO
On-Page SEO focuses on everything users and search engines see on your website pages. Its primary goal is to ensure that content clearly matches user intent and delivers value in a structured, easy-to-understand way.
1. Content Optimization:
- In 2026, content optimization means more than adding keywords. It involves creating helpful, accurate, and up-to-date content that fully answers user questions.
- Search engines evaluate whether content demonstrates clarity, depth, and real understanding of the topic. Well-optimized content explains concepts naturally, avoids unnecessary fluff, and stays aligned with what users actually want to know.
- Content is also expected to be fresh. Updating old pages with new insights, current data, and improved explanations helps maintain relevance and trust.
2. Keyword Intent Alignment :
- Keywords are no longer just search terms they represent user intent. On-Page SEO now focuses on aligning content with informational, navigational, commercial, or transactional intent. This means understanding why a user is searching and structuring content to match that purpose.
- For example, an informational query needs education and clarity, while a transactional query needs clear calls to action and trust signals. When intent is matched correctly, engagement improves and rankings become more stable.
3. Headings, Internal Linking, and UX
- Clear headings help both users and search engines understand content structure. Proper use of headings improves scannability and allows users to quickly find answers.
- Internal linking connects related content, helping users explore deeper and helping search engines understand topic relationships.
- User experience (UX) is now a core On-Page factor. Pages must be easy to read, logically organized, and free from distractions. If users struggle to navigate or consume content, rankings suffer even if the content itself is good.
Off-Page SEO
Off-Page SEO focuses on how your website is perceived outside your own domain. It is primarily about building authority, trust, and reputation across the web.
1. Authority Building:
- Authority is earned when other credible sources recognize your website as valuable. In 2026, authority is not built overnight or through shortcuts.
- It develops through consistent publishing of high-quality content, industry relevance, and genuine recognition.
Search engines look for signals that indicate your brand is respected and referenced within its niche.
2. Backlinks and Brand Mentions:
- Backlinks remain important, but their quality matters far more than quantity. Links from trusted, relevant websites signal credibility.
- Even unlinked brand mentions contribute to trust by showing that your brand is being discussed naturally. Spammy or manipulative link practices no longer work and can harm visibility. Off-Page SEO today is about earning links, not building them artificially.
3. Trust and Reputation Signals:
- Trust extends beyond links. Reviews, citations, expert mentions, and consistent brand presence across platforms all contribute to reputation. Search engines evaluate whether users and authoritative sources view a business as reliable and legitimate.
- A strong reputation increases confidence—not only for search engines but also for users deciding whether to engage.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO ensures that your website is accessible, fast, and understandable for search engines while delivering a smooth experience for users.
1. Site Performance and Core Web Vitals:
- Performance is a ranking factor in 2026. Pages must load quickly, respond smoothly, and remain visually stable. Core Web Vitals measure real user experience related to speed, interactivity, and layout stability.
- Poor performance leads to higher bounce rates and lower trust. Optimizing images, reducing unnecessary scripts, and using efficient hosting are essential technical practices.
2. Mobile Friendliness:
- With most searches happening on mobile devices, mobile-first design is no longer optional.
- Websites must adapt seamlessly to different screen sizes, offer easy navigation, and maintain readability without zooming or scrolling issues.
- Search engines evaluate mobile usability as a primary ranking factor, making responsive design a foundational requirement.
3. Crawlability and Indexation:
- Search engines must be able to crawl and index your pages easily. Clean site architecture, proper internal linking, correct use of tags, and accessible resources help search engines understand what content should be indexed.
- If important pages are blocked, duplicated, or poorly structured, they may never rank regardless of content quality.

Paid Search vs Organic Search
Differences Between SEO and PPC
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization): Organic search traffic comes from SEO (Search Engine Optimization). It focuses on earning visibility naturally by creating high-quality content, improving website experience, and building trust over time. Rankings are not paid for; they are earned based on relevance, usefulness, and authority.
- PPC ( Pay-Per-Click) : Paid search comes from PPC (Pay-Per-Click) advertising, where businesses pay to appear at the top or bottom of search results for specific keywords. Visibility is immediate, but it depends entirely on budget. Once the ads stop, the traffic stops.
Cost Structure Comparison:
- SEO is often seen as “free,” but in reality, it is an investment of time, expertise, and resources. Costs may include content creation, technical improvements, tools, and skilled professionals. However, once pages rank, they can generate traffic continuously without paying for each click.
- PPC follows a direct cost model. Every click has a price, and competitive keywords can be expensive. Costs increase as competition grows, and budgets must be maintained consistently. There is full control over spending, but there is also ongoing dependency on ad budgets.
- Over time, SEO usually offers a lower cost per acquisition, while PPC provides faster but more expensive traffic.
Traffic Quality and Long-Term Sustainability:
- Organic search traffic is often high-intent and trust-driven. Users tend to trust organic results more because they are earned, not paid placements. SEO traffic compounds over time, making it more sustainable and scalable for long-term growth.
- Paid search traffic is highly targeted and effective for short-term goals like promotions, launches, or seasonal offers. However, it lacks long-term sustainability. Once campaigns pause, visibility disappears.
- In 2026, brands that rely only on paid search often struggle with rising costs, while those with strong SEO foundations benefit from consistent visibility and credibility.
When SEO and Paid Search Work Best Together:
- The most successful digital strategies do not choose between SEO and paid search—they combine both intelligently. Paid search can deliver immediate data about keywords, conversions, and user behavior. This data can then inform SEO strategies.
- At the same time, SEO strengthens brand trust, which improves paid ad performance. Users are more likely to click ads from brands they recognize organically.
Together, SEO and PPC:
- Cover both short-term and long-term goals
- Improve overall search visibility
- Reduce dependency on ads over time
- Increase conversion confidence
What Is the Role of SEO in Digital Marketing?
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) plays a central and strategic role in digital marketing, especially in 2026, where user intent and experience define success.
- SEO is not just about rankings; it is about understanding what users are searching for, why they are searching, and how businesses can meet those needs effectively.
- It acts as the bridge between user demand and digital visibility. SEO helps businesses reach users at the exact moment of intent when they are looking for information, solutions, or services.
- By analyzing search behavior and demand, SEO guides content creation, website structure, messaging, and even paid advertising strategies. This makes digital marketing more data-driven and user-focused rather than assumption-based.
- Across the marketing funnel, SEO supports awareness by answering problem-based searches, builds consideration through informative and comparison-focused content, and drives conversions with intent-matched landing pages.
- It also strengthens trust by emphasizing content quality, expertise, and transparency, which users expect from reliable brands. In addition, SEO improves user experience by focusing on fast loading pages, mobile friendliness, clear navigation, and helpful content structure.
- These factors not only improve rankings but also increase engagement and conversions. In short, SEO is the foundation of sustainable digital marketing.
- It aligns user needs with business goals, builds long-term visibility, and ensures consistent growth in an increasingly competitive digital landscape.
SEO as the Foundation of Digital Marketing
SEO acts as the foundation of digital marketing because it is built on real user data, not assumptions. Every search represents a genuine need, question, or intent, and SEO captures this data to guide smarter marketing strategies. Instead of guessing what audiences want, businesses use SEO insights to understand how people search, what language they use, and what problems they want to solve.
1.SEO data guiding content, ads, and UX:
- SEO data reveals high-intent keywords, common questions, and user behavior patterns. This information helps shape content topics, ad copy, landing pages, and website structure.
- Content teams use SEO data to create relevant blogs and resources, paid marketing teams use it to target the right audiences with the right messaging, and UX teams use it to improve navigation, clarity, and engagement.
- This alignment ensures a consistent and user-focused digital experience.
2. Search demand shaping marketing decisions:
- Search demand reflects real market interest. When many users search for a topic or solution, it signals opportunity.
- SEO helps businesses prioritize products, services, campaigns, and content based on what users actively want, making digital marketing decisions more data-driven, efficient, and results-oriented.
SEO Across the Digital Marketing Funnel
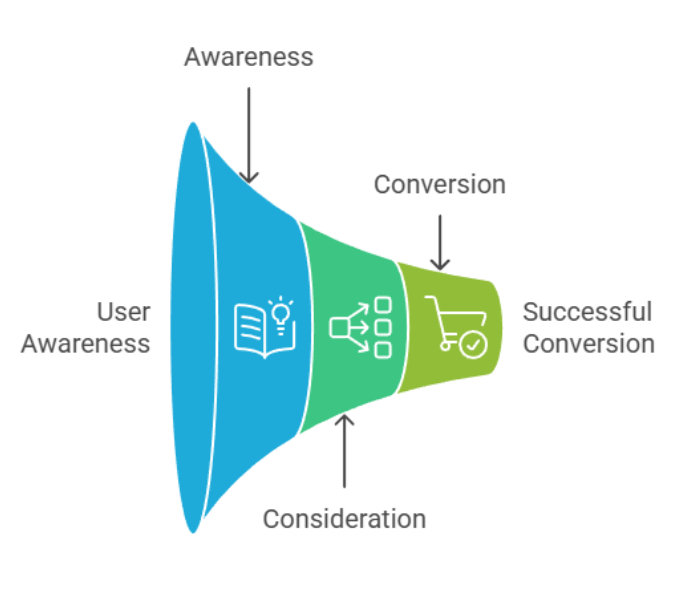
SEO plays a critical role across the entire digital marketing funnel by supporting users at every stage of their decision-making journey from awareness to conversion. In 2026, effective SEO is about delivering the right content at the right time, aligned perfectly with user intent.
1. Awareness Stage
- At the awareness stage, users are experiencing a problem or curiosity and are looking for information, not products or brands. These are problem-based searches, such as “why,” “what,” or “how” questions.
- SEO helps brands appear early by creating educational, user-friendly content that directly addresses these concerns.
Top-of-funnel content includes blogs, guides, and explainers that focus on solving problems and building understanding. The goal here is visibility and trust, not selling. - Well-structured content also increases chances of appearing in featured snippets and AI overview visibility, where search engines display direct answers. This positions the brand as a credible source, even before users click.
2. Consideration Stage
- In the consideration stage, users compare options and explore solutions. SEO supports this phase through comparison and solution-focused content such as “best options,” pros and cons, and detailed guides.
- Strong internal linking and topical authority help guide users through related content, keeping them engaged and informed.
- The role of E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) is crucial here. Content that demonstrates real expertise and transparency builds confidence and helps users move closer to a decision.
3. Conversion Stage
- During the conversion phase, customers are ready for action. SEO ensures intent-matched landing pages that align with transactional searches. Page experience impact—speed, mobile usability, and clarity—directly influences conversions.
- Using insights from SEO data, businesses make SEO-driven CRO improvements that reduce friction and increase successful outcomes.
SEO as the Backbone of Digital Marketing Channels
- SEO acts as the strategic backbone of digital marketing because it is rooted in real user behavior and search demand. Instead of relying on assumptions or trends alone, SEO provides clear insights into what people are actively looking for, how they search, and what type of content they prefer.
- This makes all marketing efforts more focused, efficient, and aligned with user needs. Among all channels, content marketing benefits the most from SEO because content is the primary way users interact with search results.
SEO and Content Marketing
SEO and content marketing work together to ensure content is not only well-written but also discoverable, relevant, and valuable to the target audience.
1 . Human-First Content Strategy:
- In 2026, SEO strongly supports a human-first content strategy. Instead of writing for algorithms, content is created to solve real problems, answer questions clearly, and guide users with honest information.
- Search engines now prioritize content that demonstrates usefulness, clarity, and experience. When content genuinely helps users, it naturally aligns with SEO goals and earns long-term visibility.
2. Topic Clusters vs Isolated Posts
- Modern SEO favors topic clusters over isolated blog posts. Topic clusters organize content around a central theme, supported by related subtopics that are internally linked.
- This structure helps users explore a subject in depth and signals topical authority to search engines. In contrast, isolated posts often lack context and struggle to maintain consistent rankings.
3. Content Planning Using Real Demand
- SEO data reveals actual search demand what users want, how often they search, and what questions they ask.
- This allows marketers to plan content based on real user interest, not guesswork. As a result, content marketing becomes more strategic, sustainable, and performance-driven.
SEO and Paid Advertising
SEO and paid advertising work best when they support each other rather than operate separately. SEO provides deep insights into user intent, keyword performance, and content effectiveness, which can significantly improve the efficiency of paid campaigns.
Reducing ad costs using SEO insights: SEO data helps identify high-performing keywords, search intent patterns, and user behavior before money is spent on ads. By targeting keywords that are already proven to attract engaged users organically, advertisers can avoid wasting budget on low-intent or irrelevant clicks. This results in better targeting, higher click-through rates, and reduced cost per acquisition.
Organic rankings for high CPC keywords: Many competitive keywords have a high cost-per-click. Strong organic rankings for these high-CPC keywords reduce dependency on paid ads while maintaining visibility. Over time, SEO becomes a cost-saving channel by delivering consistent traffic without paying for every click, allowing paid budgets to be used more strategically.
Landing page quality score benefits: SEO-optimized landing pages focus on relevance, clarity, and user experience—key factors that improve quality scores in paid advertising platforms. Better page structure, faster load times, and intent-matched content lead to higher engagement and conversions, improving ad performance and lowering overall advertising costs.
SEO and Social Media
SEO and social media support each other by strengthening brand visibility, trust, and discoverability across the digital ecosystem. While social media signals are not direct ranking factors, their impact on user behavior and brand awareness plays an important role in SEO success.
Brand search growth: Consistent and engaging social media activity increases brand awareness. As users repeatedly see a brand on social platforms, they are more likely to search for it directly on search engines. This growth in branded searches is a strong trust signal, indicating brand recognition and credibility, which supports long-term SEO performance.
Indirect SEO benefits of social signals: Social media allows the quick growth of content’s audience. When content is shared, discussed, and engaged with, it gains visibility that can lead to backlinks, mentions, and increased traffic. These indirect effects strengthen authority and relevance, even though social signals themselves are not direct ranking factors.
Discoverability beyond platforms : Social media content has a short lifespan, but SEO extends its value. By optimizing content for search, brands ensure their ideas, messaging, and resources remain discoverable long after social posts disappear from feeds. SEO turns short-term social visibility into long-term digital presence.
SEO and Email Marketing
SEO and email marketing work together to build sustainable audience growth and long-term engagement. SEO attracts users at the moment of interest, while email marketing nurtures those users into loyal subscribers and customers.
SEO-driven lead magnets: SEO helps identify topics users actively search for, allowing businesses to create lead magnets such as guides, checklists, or resources that directly match user intent. When these assets are optimized for search, they attract highly relevant visitors who are more likely to subscribe, resulting in better-quality leads.
Evergreen content for nurturing: SEO-focused evergreen content continues to attract traffic over time and can be reused within email campaigns. Blogs, tutorials, and guides that remain relevant help nurture subscribers by educating them, answering common questions, and building trust throughout the customer journey.
Search traffic as a list growth engine: Organic search traffic becomes a powerful list growth engine because it brings users who already have a genuine interest in the topic. By strategically placing sign-up opportunities within SEO-optimized content, businesses consistently grow their email lists with engaged, high-intent subscribers.
Core SEO Activities That Drive Digital Marketing Results
SEO delivers real digital marketing results when it is executed through clear, practical, and intent-focused activities. Among all SEO tasks, keyword research remains one of the most critical because it reveals what users want, how they search, and where business opportunities exist. In 2026, keyword research is less about finding words and more about understanding user intent and demand patterns.
Keyword Research
Keyword research is the foundation of every successful SEO and digital marketing strategy. It helps businesses identify the exact questions, problems, and goals users express through search. Modern keyword research focuses on meaning, context, and intent rather than just search volume.
Search Intent Mapping:
- Search intent mapping involves classifying keywords based on what users are trying to achieve informational, navigational, commercial, or transactional. This process ensures that each keyword is matched with the right type of content.
- For example, informational searches need educational content, while transactional searches require optimized landing pages.
By mapping intent correctly, businesses avoid mismatched content that fails to engage users. - This improves click-through rates, user satisfaction, and conversion potential, making SEO efforts more effective across the digital marketing funnel.
Demand and Opportunity Analysis:
- Demand and opportunity analysis helps determine which keywords are worth targeting. Demand shows how many users are searching for a topic, while opportunity evaluates competition, ranking difficulty, and business relevance.
- In 2026, smart SEO strategies focus on high-intent and underserved queries areas where user demand exists but quality content is limited.
- This allows businesses to gain visibility faster, attract qualified traffic, and drive meaningful digital marketing results without competing blindly for overly saturated keywords.
Content Optimization
Content optimization in 2026 goes far beyond inserting keywords. It focuses on creating clear, meaningful, and helpful content that both users and search engines can easily understand. The goal is to satisfy user intent completely while maintaining readability and trust.
Semantic relevance: Modern search engines understand topics, relationships, and context. Semantic relevance means covering a subject comprehensively using related concepts, natural language, and supporting subtopics. This helps search engines understand the depth of content and ensures users get a complete answer, not fragmented information.
Answer-focused content blocks: Users expect quick and direct answers. Answer-focused content blocks present clear responses near the top of the page, followed by supporting explanations. This improves user satisfaction and increases chances of appearing in featured snippets and AI-generated results.
AI and human readability balance : While AI helps analyze and summarize information, content must still feel human. Clear language, logical flow, and real-world examples create trust. Successful content balances AI-friendly structure with natural, engaging human writing.
Link Building
Link building remains a powerful SEO activity, but in 2026 it is about earning trust, not manipulating rankings. Links act as signals of authority and credibility across the web.
Authority and trust signals: High-quality backlinks from relevant, trusted sources indicate that content is valuable and reliable. Search engines prioritize links that come from authoritative and contextually relevant websites rather than large volumes of low-quality links.
Brand credibility: Links and mentions strengthen brand credibility. When reputable websites reference a brand naturally, it builds trust with both users and search engines. Strong brand credibility leads to more stable rankings and long-term digital marketing success.

Technical SEO That Users Never See but Always Feel
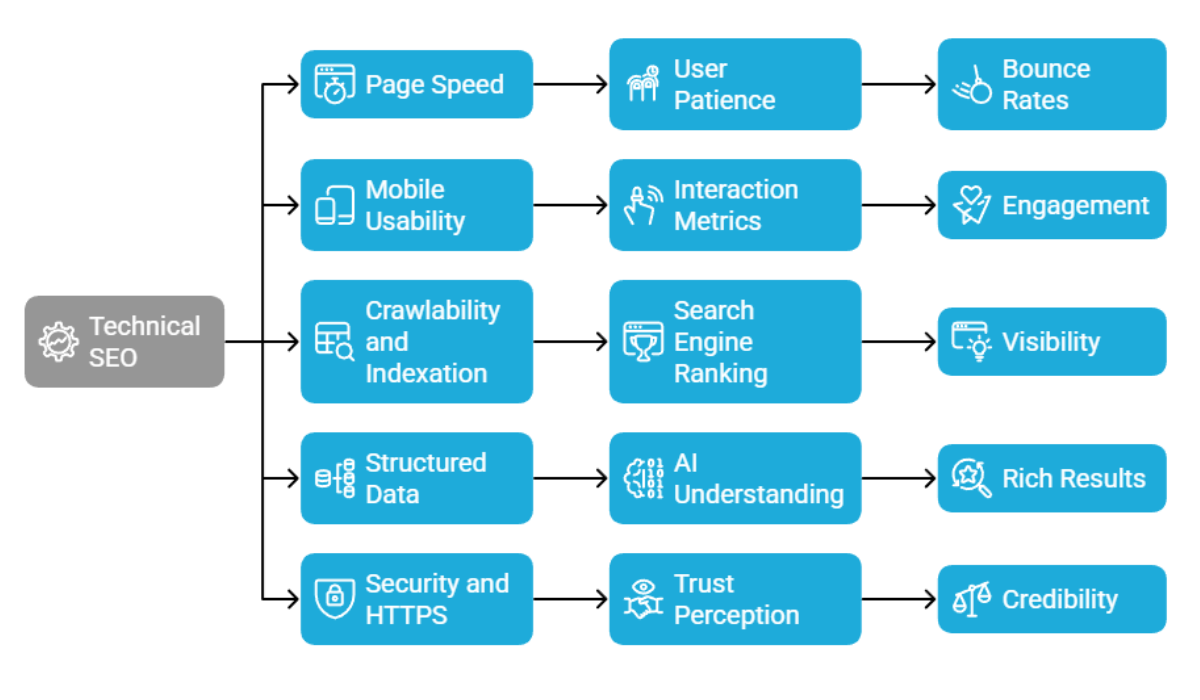
- Technical SEO works behind the scenes, but users experience its impact instantly. In 2026, visitors may not understand code or crawlability, but they immediately notice whether a website feels fast, smooth, and trustworthy.
- Page speed is critical slow sites frustrate users and increase exits, while fast pages build confidence and engagement. Mobile usability is equally important, as most users browse on smartphones and expect responsive, easy navigation.
- Clean crawlability and proper indexation ensure search engines can find and rank important pages. Structured data helps AI understand content context, and HTTPS security protects users and builds trust, creating a seamless digital experience.
1. Page Speed and User Patience :
- User patience is lower than ever. Users exit a page if it takes too long to load—often in seconds. Bounce rates, engagement, and conversions are all directly impacted by page speed.
- Search engines measure real user performance data to evaluate speed, not just technical scores. Optimized images, efficient code, fast hosting, and reduced scripts are essential. In 2026, speed is not just a ranking factor—it is a user expectation.
2. Mobile Usability and Interaction Metrics:
- Most users search and browse on mobile devices. Mobile usability now defines overall website quality. Pages must adapt smoothly to different screen sizes, offer readable text, easy navigation, and responsive elements.
- Interaction metrics such as taps, scroll behavior, and ease of use influence how search engines judge user satisfaction. A poor mobile experience leads to lower engagement and weaker SEO performance.
3. Crawlability and Indexation Hygiene:
- Content must be effectively crawled and indexed by search engines. Clean site architecture, logical internal linking, proper use of tags, and removal of duplicate or thin pages help maintain indexation hygiene.
- When search engines waste resources on irrelevant or broken pages, important content may be ignored. Strong crawlability ensures that valuable pages are discovered, understood, and ranked consistently.
4. Structured Data for AI Understanding:
- Structured data helps search engines and AI systems understand what your content means, not just what it says. By adding clear markup, websites help machines identify key information such as products, reviews, FAQs, and authorship.
- In AI-driven search environments, structured data improves eligibility for enhanced visibility, summaries, and rich results, increasing clarity and trust.
5. Security, HTTPS, and Trust Perception:
- Security is a fundamental trust signal. HTTPS encryption protects user data and reassures visitors that the site is safe. In 2026, users expect secure browsing by default.
- Any warning or security issue damages credibility instantly. Search engines favor secure websites because they protect users and demonstrate responsibility.
What Is an SEO Strategy?
- An SEO strategy is a planned, structured approach to improving a website’s visibility in search engines by aligning content, technology, and authority with user intent.
- In simple terms, it is a roadmap that defines what to optimize, why to optimize it, and how those efforts support business growth.
- In 2026, an SEO strategy is no longer about chasing rankings—it is about creating consistent value for users while achieving measurable business outcomes.
Definition of an SEO Strategy : An SEO strategy outlines how a business will attract, engage, and convert users through organic search. It includes keyword and intent research, content planning, technical improvements, internal linking, and authority building. A strong strategy ensures that every SEO action serves a clear purpose and contributes to long-term visibility, trust, and performance rather than isolated wins.
Short-Term vs Long-Term Approach:
- SEO can deliver short-term gains, such as optimizing existing pages for quick improvements, but its true strength lies in long-term growth.
- Short-term tactics focus on immediate opportunities, while long-term SEO builds topical authority, trust, and sustainable traffic. In 2026, successful brands balance both using quick wins to support business needs while investing in lasting organic presence.
Aligning SEO With Business Objectives:
- An effective SEO strategy is always aligned with business goals. Whether the objective is brand awareness, lead generation, or sales, SEO priorities are set accordingly.
- By matching search intent with business outcomes, SEO becomes a growth strategy—not just a marketing activity.
How to Set Objectives for Your SEO Strategy
- Setting clear objectives is essential for building an effective SEO strategy in 2026. SEO goals should be directly connected to business outcomes, not just rankings or traffic numbers.
- The first step is defining what success means for the business whether it is increasing brand visibility, generating qualified leads, driving sales, or expanding into new markets. These objectives guide every SEO decision.
- It is important to balance traffic and conversions. While organic traffic indicates visibility, conversions reflect real value.
Modern SEO focuses on attracting high-intent users who are more likely to take action, rather than simply increasing visitor numbers. - Businesses must also decide the balance between branding and lead generation. Branding-focused SEO builds authority and trust through informational content, while lead-driven SEO targets commercial and transactional searches.
- A well-defined objective ensures SEO efforts deliver measurable results, support long-term growth, and align seamlessly with overall digital marketing goals.
Business-Focused Goal Setting:
- SEO objectives should always align with core business goals. Instead of aiming for vague targets like “rank on page one,” businesses should define outcomes such as increasing qualified leads, improving sales, or strengthening brand visibility.
- When SEO goals are tied to revenue, customer acquisition, or market expansion, decision-making becomes clearer and more impactful.
Traffic vs Conversions:
- Traffic is important, but not all traffic delivers value. In 2026, SEO strategies prioritize quality over quantity. High-intent traffic that converts is more valuable than large volumes of irrelevant visitors.
- SEO objectives should balance attracting the right audience with optimizing content and pages to encourage actions such as sign-ups, inquiries, or purchases.
Branding vs Lead Generation:
- SEO can support both branding and lead generation, but objectives must be defined clearly. Branding-focused SEO targets visibility, authority, and trust through informational content, while lead-generation SEO focuses on transactional and commercial intent.
- A clear balance ensures SEO supports both long-term brand growth and short-term business results.
Key SEO Metrics You Should Measure
1. Organic Traffic Quality: Organic traffic quality measures how relevant your visitors are. Instead of total traffic volume, focus on metrics like pages per session, bounce rate, and returning users. High-quality traffic comes from users whose search intent matches your content and who actively engage with your website.
2. Rankings by Intent : Tracking rankings by intent is more valuable than tracking individual keywords. Monitor how your pages perform across informational, commercial, and transactional searches. This shows whether your content is visible at each stage of the buyer journey and helps identify gaps in coverage.
3. Engagement Metrics : Engagement metrics such as time on page, scroll depth, and interaction rates reveal how users experience your content. Strong engagement indicates that content is useful and easy to consume, while poor engagement highlights areas that need improvement.
4. Conversion Tracking: Conversion tracking measures how organic traffic turns into actions—form submissions, purchases, calls, or sign-ups. This metric directly connects SEO performance with business goals and helps evaluate content effectiveness.
5. ROI From SEO: Return on investment (ROI) shows the financial impact of SEO efforts. By comparing SEO costs with revenue or lead value generated from organic search, businesses can assess long-term growth, justify investment, and plan future strategies confidently.
Examples of SEO Objectives
Lead Generation Objective
- A lead generation–focused SEO objective aims to attract high-intent users and convert them into inquiries, sign-ups, or contacts. The goal is not just traffic growth but increasing qualified leads through organic search.
- This objective typically includes targeting commercial and transactional keywords, optimizing service pages, and creating problem-solution content that addresses user pain points.
- SEO efforts focus on intent-matched landing pages, clear calls to action, fast page speed, and trust signals such as testimonials and case studies.
- Success is measured through form submissions, calls, demo requests, and cost per lead from organic traffic, ensuring SEO directly supports business growth.
Brand Visibility Objective
- A brand visibility SEO objective focuses on increasing awareness, authority, and trust in search results. The aim is to ensure the brand appears consistently for informational and top-of-funnel searches related to its industry.
- This includes publishing educational blogs, guides, and thought-leadership content, as well as optimizing for featured snippets and AI-driven search results. SEO efforts target branded searches, topic authority, and wide content coverage rather than immediate conversions.
- Success is measured through impressions, branded search growth, content reach, and overall search presence, helping the brand become a recognized and trusted name over time.
Ecommerce Sales Objective
- An ecommerce SEO objective is centered on driving product visibility and online sales through organic search. The focus is on optimizing category pages, product listings, and buyer-intent keywords such as “buy,” “best,” and “price.”
- SEO efforts include improving product descriptions, structured data, page speed, mobile usability, and internal linking between products and categories. User reviews, trust badges, and clear navigation play a major role in conversions.
- Success is measured through organic revenue, conversion rate, average order value, and return on investment, ensuring SEO contributes directly to sustainable ecommerce growth.
SEO Objectives for Different Business Types
Small Businesses:
- For small businesses, SEO objectives focus on building online visibility and steady organic growth with limited budgets. The primary goal is to attract relevant local and niche audiences through intent-based keywords and helpful content.
- Small businesses aim to improve website visibility, generate consistent inquiries, and compete with larger brands by targeting low-competition, high-intent searches.
- SEO also helps establish credibility and trust, allowing small businesses to grow sustainably without heavy dependence on paid advertising.
Local Businesses :
- Local businesses use SEO to attract nearby customers who are ready to take action. The main objective is to appear in local search results and map listings for location-based queries.
- This includes optimizing for local keywords, business listings, reviews, and mobile experience. SEO helps drive foot traffic, phone calls, and appointment bookings by connecting local intent searches with nearby services at the right moment.
Ecommerce Brands:
- Ecommerce brands focus SEO objectives on increasing product visibility and driving online sales. The goal is to rank for buyer-intent keywords, optimize category and product pages, and improve user experience for conversions.
- SEO also supports long-term growth by reducing reliance on paid ads, increasing organic revenue, and building trust through reviews, content, and structured data.
Service-Based Companies:
- Service-based companies use SEO to generate qualified leads and establish authority in their industry. Objectives include ranking for service-related searches, educating potential clients through informative content, and building trust with expertise-driven pages.
- SEO supports consistent lead flow by matching user problems with clear service solutions and conversion-focused landing pages.
Local SEO and Intent-Based Discovery
Local SEO in 2026 is driven by intent-based discovery, where users search with immediate needs and strong purchase intent. These searches are highly valuable because they often lead directly to calls, visits, or bookings. Search engines now prioritize proximity, relevance, trust, and real-world signals to decide which local businesses appear first.
High-Converting Local Intent Searches:
- Local intent searches include terms like “near me,” “open now,” or service + location, indicating users are ready to take immediate action.
- These searches attract high-quality traffic because users already know what they want and are close to making a decision.
- Queries with urgency such as “emergency,” “same day,” or “best” show strong commercial intent and higher conversion potential.
- Optimizing for these keywords helps businesses capture users at the decision stage rather than the research stage.
- Mobile-driven local searches often lead to calls, visits, or bookings within hours.
- Focusing on these searches improves ROI by driving real-world conversions, not just website traffic.
Google Business Profile Optimization:
- An optimized Google Business Profile helps businesses appear in local packs, map results, and high-intent searches.
- Accurate name, address, phone number, categories, and business hours build trust and improve visibility.
- Regularly updating photos, services, and posts signals activity and relevance to search engines.
- Fresh content on the profile increases engagement and encourages user actions like calls and directions.
- Responding to customer reviews improves credibility and strengthens local ranking signals.
- A well-managed profile directly impacts conversions by making it easy for users to contact or visit the business.
Reviews as Ranking and Conversion Factors:
- Customer reviews act as strong trust and credibility signals for both users and search engines.
- Search engines consider review quality, quantity, freshness, and responses when ranking local businesses.
- Positive reviews improve click-through rates by influencing user decisions at the search results stage.
- Users are more likely to contact or visit businesses with higher ratings and recent feedback.
- Responding to reviews shows professionalism and customer care, increasing trust and engagement.
- In 2026, reviews play a direct role in both local visibility and conversion success.
Location Pages Done Right:
- Well-optimized location pages help businesses rank for multiple service areas without creating duplicate content.
- Each page should include unique local information, services offered, and clear contact details.
- Adding local testimonials, FAQs, and directions improves relevance and user trust.
- Search engines favor location pages that genuinely serve local users, not generic placeholders.
- Strong internal linking connects location pages to core services and improves crawlability.
Properly built location pages increase local visibility, engagement, and conversion rates.
Hyperlocal Content Strategy:
- Hyperlocal content targets specific neighborhoods, communities, or nearby areas with highly relevant information.
- This approach helps businesses connect directly with local audiences and stand out in competitive markets.
- Content such as local guides, area-specific services, and community-focused topics builds strong relevance.
- Search engines reward hyperlocal content that reflects real local intent and user needs.
- Hyperlocal strategies improve trust, engagement, and visibility for “near me” and location-based searches.
- In 2026, hyperlocal content drives higher conversions by matching precise local intent with useful information.
Best SEO Tools for Digital Marketers
Category | Purpose | Popular Tools | How They Help Digital Marketers |
Keyword Research Tools | Identify search demand, intent, and keyword opportunities | SEMrush, Ahrefs, Ubersuggest | Help find high-intent keywords, analyze competition, and plan SEO-driven content |
Technical SEO Tools | Analyze site health, crawlability, and performance | Screaming Frog, GTmetrix | Identify technical issues like broken links, slow pages, and indexing problems |
Analytics & Reporting Platforms | Measure traffic, engagement, and conversions | Google Analytics, Google Search Console | Track organic performance, user behavior, rankings, and SEO ROI |
Competitive Intelligence Tools | Analyze competitor strategies and market gaps | Ahrefs, SEMrush | Monitor competitor keywords, backlinks, content gaps, and growth opportunities |
Common SEO Myths That Hurt Digital Marketing
SEO is often misunderstood, and these misunderstandings can lead businesses to make poor digital marketing decisions. In 2026, SEO is more advanced and user-focused than ever, yet several outdated myths still hurt performance. Clarifying these myths helps brands build smarter, more sustainable SEO strategies.
SEO Is Not Just Rankings :
- One of the biggest myths is that SEO success is only about ranking on the first page. Rankings alone do not guarantee traffic, engagement, or conversions. Modern SEO focuses on search intent, user experience, and business outcomes.
- A lower-ranked page that matches intent and converts users can be more valuable than a top-ranking page with poor engagement.
AI Did Not Kill SEO:
- AI has changed how search works, but it has not replaced SEO. Instead, AI has made SEO more strategic. Search engines now reward clarity, usefulness, and expertise, not shortcuts.
- SEO is still essential for helping AI systems understand, trust, and surface content effectively.
More Content Does Not Equal Better Results :
- Publishing large volumes of content does not guarantee success. Low-value or repetitive content can hurt performance. In 2026, content quality, relevance, and intent alignment matter far more than quantity.
- Fewer, well-optimized pages often outperform large volumes of thin content.
Low-Quality Backlinks Do Not Help:
- Many believe any backlink improves SEO. In reality, low-quality or spammy links can damage trust and rankings.
- Search engines prioritize quality, relevance, and credibility.
- Earning fewer high-quality links is far more effective than building many weak ones.
Conclusion : Why SEO Is a Long-Term Digital Asset
SEO is not a short-term tactic or a one time campaign it is a compounding digital investment that grows stronger over time. Unlike paid marketing, where visibility stops when budgets end, SEO continues to deliver value long after the initial effort. Every optimized page, earned backlink, and improved user experience adds to a foundation that compounds visibility and performance month after month.
By consistently focusing on helpful content, technical excellence, and intent alignment, SEO helps businesses build authority, trust, and long-term visibility. Search engines reward brands that demonstrate expertise and reliability, while users return to sources they trust. This combination creates a self-reinforcing cycle of credibility and engagement.
SEO also provides a competitive advantage through organic growth. Businesses with strong organic presence are less dependent on ads, more resilient to market changes, and better positioned to capture high-intent demand.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is SEO and why is it important in digital marketing today?
SEO helps businesses appear when users search for information, products, or services. It is important because it drives long-term, high-intent traffic without paying for every click.
2. Is SEO still worth learning and investing in 2026?
Yes, SEO is more important than ever because AI-driven search still relies on high-quality, trustworthy, and intent-matched content.
3. How does SEO help generate leads and sales?
SEO attracts users who are actively searching for solutions, making them more likely to convert into leads or customers.
4. What is the difference between ppc and seo?
SEO delivers organic, long-term traffic, while paid ads provide instant visibility but stop when the budget ends.
5. How long does SEO take to show results?
SEO usually takes 3–6 months to show noticeable results, depending on competition, website quality, and strategy.
6. Does AI replace SEO or make it less important?
No, AI does not replace SEO. It increases the need for clear, helpful, and experience-based content that AI systems can trust.
7. What are the three main pillars of SEO?
The three pillars are On-Page SEO, Off-Page SEO, and Technical SEO.
8. What is user search intent and how does it impact seo ranking ?
Search intent explains why a user searches. Matching intent improves rankings, engagement, and conversions.
9. How does technical SEO affect user experience?
Technical SEO improves speed, mobile usability, security, and navigation, which users feel even if they don’t see the technical work.
10. What is page speed so important for seo and users ?
Fast pages reduce bounce rates, improve trust, and are favored by search engines using real user data.
11. What is local SEO and how does it help small businesses?
Local SEO helps businesses appear for nearby searches, driving calls, visits, and bookings from high-intent users.
12. How do reviews impact SEO and conversions?
Reviews act as trust signals, influence rankings, and strongly affect user decisions before contacting a business.
13. Does more content mean better SEO results?
No, quality matters more than quantity. Helpful, intent-focused content performs better than large volumes of low-quality pages.
14. Are backlinks still important for SEO in 2026?
Yes, but only high-quality, relevant backlinks help. Low-quality links can harm SEO.
15. How does SEO support content marketing?
SEO ensures content is created based on real search demand, making it discoverable and valuable.
16. What SEO metrics should businesses track today?
Key metrics include organic traffic quality, intent-based rankings, engagement, conversions, and SEO ROI.
17. Can SEO help with branding, not just traffic?
Yes, SEO builds long-term brand visibility, authority, and trust across search results.
What kind of skills are needed to become an SEO specialist?
Key skills include technical SEO, keyword research, analytics, content optimization, UX understanding, and strategy.
19. Is SEO a good long-term career option?
Yes, SEO offers strong career growth, high demand, and opportunities across industries.
20. Why is SEO considered a long-term digital asset?
SEO compounds over time, builds trust and authority, reduces ad dependency, and delivers sustainable organic growth.
