Generative AI vs Traditional AI
What is the main difference between Generative AI VS Traditional AI ?
- Generative AI and Traditional AI differ in their approach and capabilities.
- Traditional AI follows predefined rules and algorithms to analyze data, make decisions, and automate tasks, primarily focusing on classification, prediction, and optimization.
- In contrast, Generative AI creates new content, such as text, images, music, and code, by learning patterns from large datasets and generating outputs that mimic human creativity.
While Traditional AI is task-specific, Generative AI is more flexible and capable of producing unique, human-like responses, making it valuable for applications like content creation, design, and conversational AI.
Traditional AI vs Generative AI with Real world examples
What is Traditional AI?
Traditional AI, also known as Narrow AI or Rule-Based AI, is the type of AI that most people are familiar with. It’s designed to perform specific tasks by following predefined rules and patterns.
Think of it as a highly specialized tool that excels at one thing but can’t do much else.
How Does Traditional AI Work?
Traditional AI relies on algorithms programmed to analyze data, recognize patterns, and make decisions based on those patterns. For example:
- A spam filter in your email inbox uses Traditional AI to identify and block unwanted messages.
- A voice assistant like Siri or Alexa uses Traditional AI to understand your commands and provide answers.
- A recommendation system on Netflix uses Traditional AI to suggest movies or shows based on your viewing history.
Strengths of Traditional AI
- Traditional AI is highly accurate when it comes to specific tasks. For example, it can quickly analyze thousands of medical images to detect diseases.
- It can process large amounts of data in a short time, making it ideal for tasks like fraud detection or inventory management.
- Since it follows predefined rules, its behavior is consistent and accurate.
Limitations of Traditional AI
- Traditional AI can’t create anything new. It can only work with the data it’s been trained on.
- It’s designed for specific tasks and can’t adapt to new situations outside its programming.
- Traditional AI requires large amounts of labeled data to function effectively. Without this data, it can’t learn or improve.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a new and more advanced form of AI that goes beyond following rules. Instead of just analyzing data, it can create new content based on the patterns it has learned.
This includes text, images, music, and even videos.
How Does Generative AI Work?
Generative AI uses machine learning called deep learning, which involves neural network systems inspired by the human brain.
These networks are trained on massive datasets and learn to generate new content by identifying patterns and relationships in the data.
- ChatGPT: A Generative AI model that can write essays, answer questions, and even hold conversations.
- DALL·E: A Generative AI tool that creates images from text descriptions, like “a cat wearing a hat.”
- Deepfake Technology: A controversial application of Generative AI that can create realistic videos of people saying or doing things they never did.
Strengths of Generative AI
- Generative AI can create new content, making it useful for tasks like writing, design, and art.
- It can be applied to a wide range of fields, from entertainment to healthcare.
- Generative AI can learn from new data and improve over time, making it more flexible than Traditional AI.
Limitations of Generative AI
- The content generated by AI isn’t always accurate or reliable. For example, ChatGPT might produce plausible-sounding but incorrect information.
- Generative AI can be misused for deepfakes, fake news, or other harmful purposes.
- Training and running Generative AI models require significant computing power and energy.
Generative AI vs. Traditional AI: Key Differences
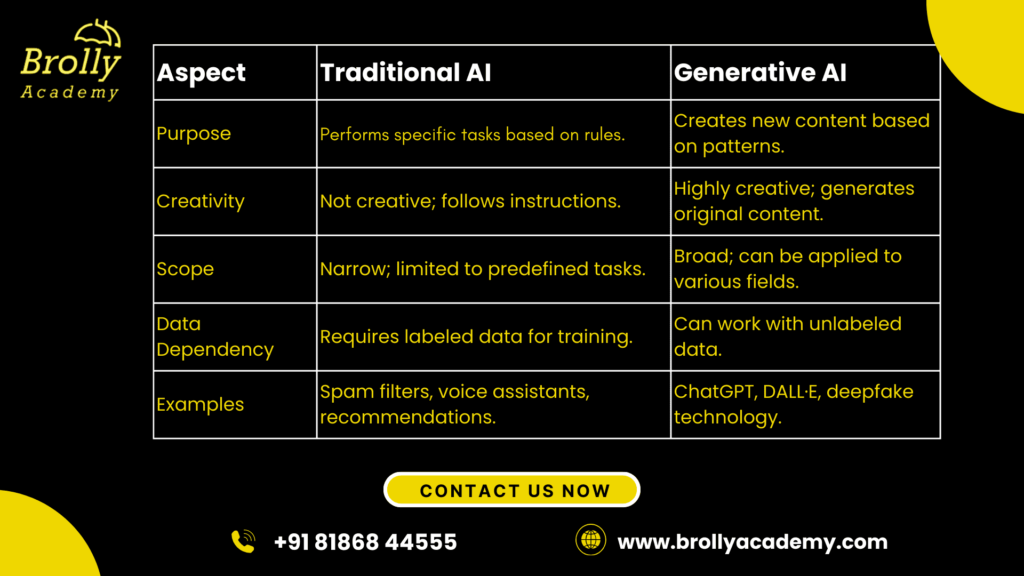
Aspect | Traditional AI | Generative AI |
Purpose | Performs specific tasks based on rules. | Creates new content based on patterns. |
Creativity | Not creative; follows instructions. | Highly creative; generates original content. |
Scope | Narrow; limited to predefined tasks. | Broad; can be applied to various fields. |
Data Dependency | Requires labeled data for training. | Can work with unlabeled data. |
Examples | Spam filters, voice assistants, recommendations. | ChatGPT, DALL·E, deepfake technology. |
Applications of Generative AI VS Traditional AI
Applications of Traditional AI
- Healthcare: Diagnosing diseases, analyzing medical images, and predicting patient outcomes.
- Finance: Detecting fraud, managing risks, and automating trading.
- Retail: Personalizing recommendations, optimizing inventory, and improving customer service.
- Manufacturing: Monitoring equipment, predicting maintenance needs, and improving efficiency.
Applications of Generative AI
- Content Creation: Writing articles, generating marketing copy, and creating social media posts.
- Art and Design: Producing digital art, designing logos, and creating animations.
- Entertainment: Composing music, writing scripts, and developing video games.
- Education: Creating personalized learning materials and generating practice questions.
Generative AI vs. Traditional AI: Which is Better? Traditional AI vs Generative AI with real-world examples
On the other hand, Generative AI performs well in tasks that require creativity and originality. If you want to create a piece of art, write a story, or design a new product, Generative AI is the better choice.
The Future of AI
- Healthcare: Traditional AI could analyze medical data, while Generative AI could create personalized treatment plans.
- Education: Traditional AI could assess student performance, while Generative AI could generate customized learning materials.
- Entertainment: Traditional AI could recommend movies, while Generative AI could create new content based on user preferences.
Ethical Considerations
Both Traditional AI and Generative AI raise important ethical questions. For example:
- Bias: AI systems can inherit biases from the data they’re trained on, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Privacy: AI often relies on large amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and security.
- Accountability: If an AI system makes a mistake or causes harm, who is responsible?
These issues highlight the need for careful regulation and oversight as AI becomes more integrated into our lives.
Responsible AI usage is critical. Learn about AI ethics from the OECD AI Observatory.
Conclusion of Generative AI vs Traditional AI
Generative AI and Traditional AI are two sides of the same coin, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Traditional AI is reliable excels at specific tasks and delivers consistent results.
Generative AI, on the other hand, is a creative powerhouse, capable of producing original content and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
As we move forward, the key will be to leverage the strengths of both types of AI while addressing their limitations and ethical challenges.
By doing so, we can unlock the full potential of AI and create a future that’s smarter, more creative, and more inclusive.
Whether you’re a business owner, a student, or just someone curious about technology, understanding the differences between Generative AI and Traditional AI is essential.
After all, AI isn’t just a tool, it’s a transformative force that’s shaping the world we live in.
FAQ’s
Generative AI vs Traditional AI
1. What is the main difference between Generative AI and Traditional AI?
Traditional AI is designed to perform specific tasks by following predefined rules and patterns (e.g., spam filters or voice assistants). Generative AI, on the other hand, can create new content, such as text, images, or music, by learning patterns from data (e.g., ChatGPT or DALL·E).
2. Can Generative AI replace Traditional AI?
No, Generative AI cannot replace Traditional AI because they serves different purposes.
Traditional AI is better for tasks requiring accuracy and efficiency, like data analysis or fraud detection, while Generative AI excels in creative tasks like content creation or design.
3. Is Generative AI more advanced than Traditional AI?
Generative AI is more advanced in terms of creativity and versatility, but it’s not necessarily “better.” Traditional AI is still more effective for rule-based, repetitive tasks.
Both have their own strengths and are used in different scenarios.
4. What are some real-world examples of Traditional AI?
Examples of Traditional AI include:
- Spam filters in email.
- Voice assistants like Siri or Alexa.
- Recommendation systems on Netflix or Amazon.
- Fraud detection systems in banking.
5. What are some real-world examples of Generative AI?
Examples of Generative AI include:
- ChatGPT for writing and answering questions.
- DALL·E for generating images from text descriptions.
- Deepfake technology for creating realistic videos.
- AI tools that compose music or write stories.

