Purpose of Prompt Engineering in Gen AI Systems
1. Introduction to Prompt Engineering
- Prompt engineering is a specialized technique within artificial intelligence, particularly generative AI, that focuses on crafting precise and effective prompts to optimize the output of AI models.
- In simple terms, it is the process of creating well-structured instructions that enable AI systems to generate accurate, relevant, and contextually appropriate responses.
- The rise of large language models (LLMs) like GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 has amplified the importance of prompt engineering.
- Unlike traditional programming, where algorithms are clearly written, generative AI relies on human input in the form of prompts to function.
- These prompts act as guides for the AI, influencing its understanding and response generation.
- For instance, asking a model, “Describe the importance of renewable energy” might produce a general response.
- However, refining the prompt to “Explain the environmental and economic benefits of renewable energy in under 300 words” can lead to a far more focused and concise answer.
- Prompt engineering bridges the gap between user intent and AI output, ensuring that the interaction is meaningful and productive.
2. What Are Generative AI Systems?
- Generative AI systems are advanced artificial intelligence models designed to create new, original content across various domains.
- Unlike traditional AI models that analyze data and provide classifications or predictions, generative AI systems produce outputs such as text, images, music, videos, and even programming code.
- These systems leverage complex algorithms to learn patterns from vast datasets, enabling them to mimic human-like creativity and problem-solving capabilities.
- Generative AI operates on deep learning principles, particularly transformer-based architectures.
- Transformers, such as those used in models like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) or DALL-E, excel at processing sequential data, making them ideal for tasks requiring contextual understanding and generation.
- For example, a language model like GPT generates text by predicting the next word in a sequence, informed by the context of previous words.
- GPT Models: Used for generating human-like text for applications such as chatbots, content creation, and summarization.
- DALL-E and Stable Diffusion: Generate realistic images based on textual descriptions.
- Codex: Specializes in generating programming code based on natural language prompts.
- Content Creation: Writing articles, marketing copy, and social media posts.
- Design and Art: Producing visual art and graphic designs.
- Education: Creating personalized learning materials and assessments.
- Healthcare: Assisting with diagnostics and report generation.
Discover the purpose of Prompt Engineering in Generative AI Systems with Brolly Academy. Master the skills, unlock AI’s potential, and gain practical expertise with hands-on learning. With expert guidance and 100% placement assistance, we help you shape a thriving career in the AI industry. Enroll now and lead the future of technology,
We will provide Machine Learning training with Generative AI
3. The Role of Prompts in AI Communication
Purpose of Prompt Engineering in Gen AI Systems
- Prompts are the essential communication medium between users and generative AI systems.
- They serve as the starting point for AI to interpret user intent and produce meaningful responses.
- A prompt is essentially a set of instructions or a query provided to the AI model, guiding it to deliver output that matches the user’s expectations.
- Generative AI models, such as GPT or DALL-E, operate by analyzing input data and generating results based on their training.
- However, these systems do not possess internal understanding; instead, they rely on prompts to contextualize and tailor their outputs. For example:
- A prompt like ‘Explain the concept of photosynthesis” will result in a basic explanation.
- A more detailed prompt like “Write a 200-word essay on photosynthesis suitable for a middle-school science project” will yield a precise, tailored response.
- Clarity: The prompt must clearly convey the user’s intent to avoid deviations.
- Context: Providing relevant background information helps the AI model understand the scope of the task.
- Specificity: Clearly defining the desired output format or tone ensures the AI meets expectations.
- Constraints: Including word limits, formatting rules, or stylistic preferences can further refine the results.
- Prompts not only determine the content of the output but also influence its quality and relevance.
- A vague or poorly constructed prompt may result in incomplete or off-topic responses, whereas a detailed and well-structured prompt enhances coherence and depth.
- By acting as the bridge between human users and AI systems, prompts empower users to extract maximum value from generative AI models, making prompt engineering a pivotal aspect of effective AI communication.
4. How Prompt Engineering Enhances Generative AI Performance
Purpose of Prompt Engineering in Gen AI Systems
- Prompt engineering is critical in maximizing the efficiency, accuracy, and usability of generative AI systems.
- By carefully crafting prompts, users can guide AI models to produce high-quality outputs that align with specific objectives.
- This process not only improves the relevance of the generated content but also ensures that the AI meets contextual and stylistic expectations.
- Improved Contextual Understanding
Generative AI systems are only as effective as the prompts they receive. - A well-engineered prompt provides the AI with context, allowing it to interpret user intent accurately.
- For instance, the prompt “Describe the benefits of AI in healthcare” is informative but broad, while “Write a 300-word essay on how AI improves diagnostics in healthcare” specifies both context and scope, resulting in a more precise response.
2. Tailored Output Generation
Prompt engineering enables users to define the tone, style, and structure of the output. Whether it’s formal, conversational, or technical, an effective prompt ensures the AI generates content that matches the intended audience and purpose. For example:
- Formal: “Summarise the key challenges in global climate policy in a professional tone.”
- Conversational: “Explain climate change to a 10-year-old in a friendly tone.”
3. Efficiency and Accuracy
Refined prompts reduce the need for repeated queries or manual corrections. By anticipating potential deviations and specifying requirements upfront, prompt engineering minimizes irrelevant or inaccurate outputs, saving time and effort.
- 4. Exploration of Creative Possibilities
Generative AI models excel in creative tasks, but prompt engineering helps focus their creativity. - For instance, a vague instruction like “Create a story” may yield generic results, whereas a detailed prompt like “Write a 500-word mystery story set in 19th-century London, featuring a detective” encourages the model to produce richer and more engaging content.
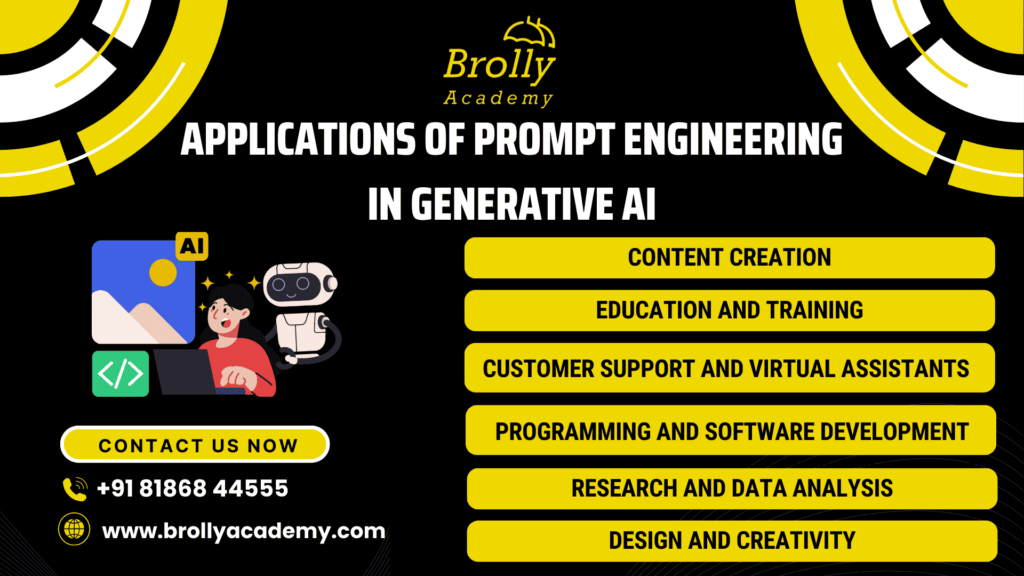
5. Applications of Prompt Engineering in Generative AI
1. Content Creation
Generative AI excels in producing high-quality content across different formats. Prompt engineering allows users to create detailed and engaging outputs by specifying the type, tone, and structure of the content. Examples include:
- Writing blog posts, articles, or essays.
- Crafting marketing copy, product descriptions, or social media captions.
- Generating poetry, stories, or scripts with predefined themes or styles.
2. Education and Training
In educational contexts, prompt engineering helps create personalized learning materials. Teachers and trainers can use generative AI to:
- Generate quizzes and assignments tailored to specific topics.
- Summarize complex topics for different learning levels.
- Simulate conversations for language learning or skill development.
Purpose of Prompt Engineering in Gen AI Systems
3. Customer Support and Virtual Assistants
Customer service applications rely on precise prompts to ensure helpful and accurate responses. Prompt engineering enables:
- Improved chatbot conversations through context-specific queries.
- Personalization of responses to cater to individual customer needs.
- Automation of routine tasks like order tracking and FAQs.
4. Programming and Software Development
Generative AI systems, like Codex, use prompt engineering to enhance productivity in software development. Key applications include:
- Generating code snippets based on user input.
- Debugging and suggesting optimizations.
- Documenting software functionality automatically.
5. Research and Data Analysis
In research, prompt engineering aids in extracting insights and summarizing information. Researchers use generative AI for:
- Literature reviews and data summaries.
- Hypothesis generation and exploration.
- Simulation of scenarios for predictive analysis.
6. Design and Creativity
Generative AI can produce visual, audio, or multimedia content based on carefully crafted prompts. Applications include:
- Designing graphics, logos, or advertisements.
- Composing music or soundtracks.
- Generating concept art or storyboards for films and games.
6. Challenges in Prompt Engineering
Purpose of Prompt Engineering in Gen AI Systems
Generative AI models, while powerful, are not inherently intelligent. They are based on training data-derived probabilistic patterns. This often leads to unpredictable behavior when prompts are ambiguous or too complex. For instance:
- A vague prompt like “Explain AI” may result in overly broad responses.
- An overly detailed prompt can confuse the model, causing irrelevant or incomplete outputs.
Inconsistent prompt wording may result in unexpected consequences. For example, the phrase “Explain AI ethics” could be interpreted as:
- A discussion about ethical concerns in AI development.
Generative AI models are limited by the data they were trained on. If a prompt addresses a niche or unfamiliar topic, the AI might:
- Provide incomplete or inaccurate responses.
- Default to generalizations that lack depth.
Creating an effective prompt often involves multiple iterations. Users may need to test and adjust prompts repeatedly to achieve the desired outcome. This trial-and-error process can be time-consuming, especially for complex tasks.
Generative AI models may inadvertently produce biased or inappropriate content if the prompts are poorly worded or the training data contains biases. Prompt engineers must be vigilant in crafting inclusive and neutral prompts to mitigate this risk.
For organizations using generative AI at scale, ensuring consistent quality in prompts across different tasks and team members is a significant challenge. Training and standardizing prompt engineering practices are essential to maintain efficiency.
Discover the purpose of Prompt Engineering in Generative AI systems with Brolly Academy. Master the skills, unlock AI’s potential, and gain practical expertise with hands-on learning. With expert guidance and 100% placement assistance, we help you shape a thriving career in the AI industry. Enroll now and lead the future of technology
7. Best Practices for Effective Prompt Engineering
- Be Clear and Specific: Clearly state the task or question to avoid ambiguity. A specific prompt provides the AI with a well-defined objective.
- Provide Context: Including relevant background information helps the AI understand the task better.
- Use Step-by-Step Instructions: Breaking down tasks into smaller steps can lead to better results.
- Define the Desired Output Format: Specify the format, tone, or structure of the output
- Set Constraints: Limit the scope of the output to align with your requirements. Examples include word limits, style preferences, or focusing on a specific audience.
- Iterate and Refine: Prompt engineering often requires experimentation. Start with a basic prompt and refine it based on the AI’s response. Adjust wording, add details, or reframe the task if needed.
- Incorporate Examples: Providing examples within the prompt can guide the AI toward the desired response style.
- Anticipate and Address Ambiguities: Think about possible misinterpretations and clarify them in the prompt.
9. Test in Real-World Scenarios: Evaluate how the prompt performs in practical applications. For instance, test how a customer service chatbot responds to prompts in different contexts to ensure consistency and relevance.
8. The Future of Prompt Engineering in Generative AI Systems
Purpose of Prompt Engineering in Gen AI Systems
- Adaptive AI Models: Future generative AI models are likely to become more adaptive, requiring less rigid prompts. Instead of relying on precise instructions, AI systems might interpret vague or incomplete prompts using advanced context-awareness.
- Automated Prompt Optimization: Emerging tools and algorithms are being developed to assist in crafting optimal prompts. These systems could analyze user queries, suggest improvements, and automatically generate the most effective prompts.
- Personalized AI Interactions: AI systems are likely to incorporate personalization, where they learn individual users’ preferences over time. This will enable prompts to be simpler, as the AI can infer context and intent based on past interactions.
- Integration with Multimodal Systems: As generative AI expands to include multimodal systems (text, image, video, and audio generation), prompt engineering will need to accommodate multiple input types.
5. Ethical Considerations and Bias Mitigation
The future of prompt engineering will focus on minimizing biases and ensuring ethical outputs. Advanced techniques might involve:
- Detecting and correcting biased prompts.
- Enforcing ethical guidelines during prompt formulation to prevent misuse of AI.
- Collaborative AI Development: Incorporating AI systems into collaborative environments, such as software development or content creation teams, will require more specialized prompts.
- Expanding Educational Applications: The role of prompt engineering in education is expected to grow, enabling AI to create dynamic, personalized learning experiences.
8. Industry-Specific Innovations
Prompt engineering will evolve to address the unique requirements of specific industries. For example:
- Healthcare: Generating patient-friendly explanations of medical reports.
- Law: Crafting legal documents or case summaries.
- Finance: Producing accurate and regulation-compliant reports.
Conclusion
of Purpose of Prompt Engineering in Gen AI Systems
As the field of generative AI continues to evolve, prompt engineering will remain a key skill, helping AI systems become more adaptive, personalized, and capable of handling a wider range of tasks across industries. Despite the challenges that come with prompt engineering, such as ambiguity and model limitations, following best practices and continuously refining techniques will lead to better results.
Discover the purpose of Prompt Engineering in Generative AI Systems with Brolly Academy. Master the skills, unlock AI’s potential, and gain practical expertise with hands-on learning. With expert guidance and 100% placement assistance, we help you shape a thriving career in the AI industry. Enroll now and lead the future of technology

